Modifying Instance Templates and Virtual Networks¶
To quickly deploy pre-configured Dataiku instances, or complete fleets, you can use a Fleet blueprint. A Fleet blueprint uses pre-configured instance templates and virtual networks.
Instance templates tell Fleet Manager how to deploy the Dataiku DSS (Dataiku) instances linked to the template. Virtual networks tell Fleet Manager where to deploy your Dataiku instances.
You can modify your instance templates and virtual networks and create new ones. Instance templates are not tied to a specific virtual network. Fleet Manager lets you know if the modifications you make to the properties of an instance template or virtual network require reprovisioning your Dataiku instances to take effect.
Note
Before making any modifications, there are essential considerations including the impact of upgrading or reprovisioning an instance.
In this article, we’ll walk through the steps required to modify the settings in your instance templates and virtual networks.
Creating or Modifying an Instance Template¶
A Dataiku instance is always launched from an instance template. The Dataiku instance(s) you deploy from the same instance template have common properties. To modify these common properties, modify the instance template settings and then reprovision each instance linked to the template.
To view an instance template:
Launch Fleet Manager.
Under Settings, choose Instance templates.
You can create a new template or choose to modify an existing template.
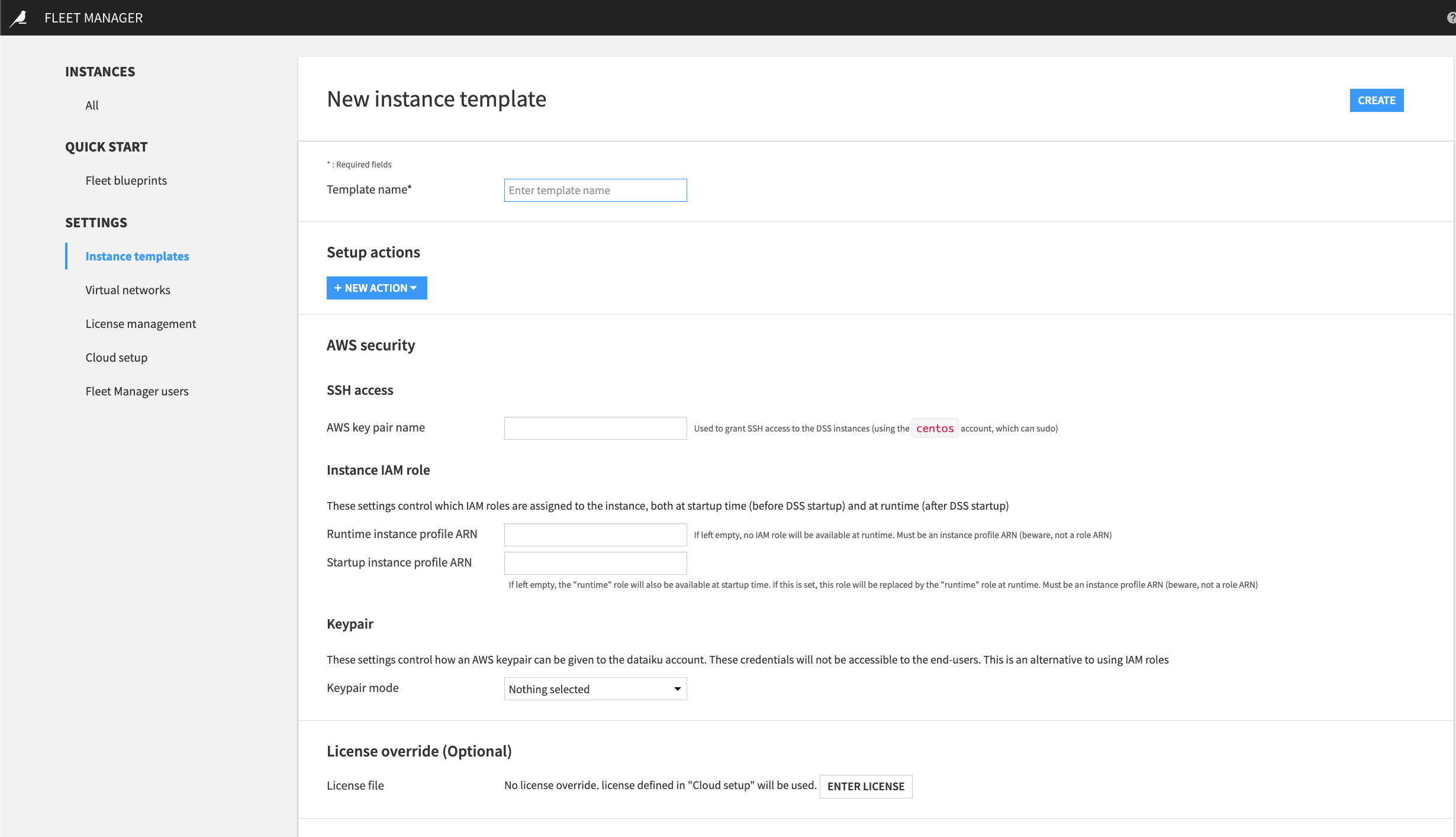
Setup Actions¶
Setup actions are configuration steps run by the Fleet Manager agent. You use setup actions to define the actions you want the Fleet Manager agent to execute on each instance linked to the template.
Setup actions allow you to configure the instance(s).
Note
Fleet Manager runs setup actions each time the instance is reprovisioned. Therefore, Setup actions should be idempotent. A Setup action is idempotent if the action can be run each time you reprovision the instance, resulting in the same expected outcome each time.
Add a New Setup Action¶
To add a new action to your instance template:
Under Settings > Instance templates, choose the instance template you want to modify.
Under Setup actions, select the New Action menu arrow to display the list.
Choose an action.
Configure the action and select Save.
Install System Packages
You can direct the Fleet Manager agent to install operating-system-level packages at the startup of each instance that is linked to the template. To do this:
Under Setup actions, choose Install system packages.
In Packages to install, specify the packages you want to install on the instance, making sure to input only one package name per line.
Add Authorized SSH Key
The SSH access defined in the Security section is limited to one SSH access key. You can authorize additional SSH keys using Setup actions.
To do this:
In Setup actions, choose Add authorized SSH Key.
In SSH Key, provide an SSH public key.
Repeat for each SSH key you want to add.
Set Up Advanced Security
You can set up security-related HTTP headers to be applied to each instance linked to the template.
Prevent Embedded Content from Rendering
You can prevent Dataiku from being embedded as an iframe or object by turning on basic headers. To do this:
Under Setup actions, choose Set security-related HTTP headers.
Toggle Basics headers to On.
Enforce HTTP Strict Transport Security
Under Setup actions, choose Set security-related HTTP headers.
Toggle HSTS to On.
Install a JDBC Driver
Dataiku instances deployed through Fleet Manager already include drivers for PostgreSQL, Snowflake, and MariaDB. You can install additional JDBC drivers for each instance linked to the template.
To do this:
Under Setup actions, choose Install a JDBC driver.
In Database type, choose a database.
Optional configuration settings:
In URL, enter the full address where Fleet Manager will download the driver archive from.
In Paths in archive, add all the paths to find the JAR files in the driver archive.
This field is required when the driver is shipped as a tarball or ZIP file.
Paths are relative to the top of the archive.
Wildcards are supported.
This is useful when the archive contains instructions or other files that are not required for the driver to work.
In HTTP Headers, add the headers required to access the source which the driver is downloaded from.
This field is only needed if you download the driver from an HTTP(S) endpoint, otherwise, it is ignored (and you need to add headers to the HTTP request).
Type one header per line using “NAME: VALUE” format.
In HTTP Username, add the username.
This field is only needed if the HTTP(S) endpoint expects basic authentication.
To explicitly specify which Assigned Identity to use (when the machine has several), use the client_id.
To authenticate with a SAS Token on Azure Blob Storage (not recommended), type
token.
In HTTP Password, add the password.
This field is only needed if the HTTP(S) endpoint expects basic authentication.
To authenticate with a SAS Token on Azure Blob Storage (not recommended), store the token in this field.
In Datadir subdirectory, set the name of the subdirectory.
This field is not required for most drivers. The driver will be placed in data_dir/lib/jdbc.
Some drivers are shipped with multiple JAR files. In this case, you may want to install them under an additional level in the lib/jdbc directory.
Run Ansible Tasks
You can run a list of Ansible tasks as if they were a role executed by a playbook targeting the host(s).
Each Dataiku instance is configured with Dataiku’s Ansible Module that allows you to configure Dataiku including its connections, settings, and projects through a YAML description.
If you want to apply more settings, you can leverage any builtin Ansible modules.
To run an Ansible task:
Under Setup actions, choose Run Ansible tasks.
In Stage, select the stage where you want the Ansible tasks to run.
Before DSS install.
After DSS install.
After DSS is started.
In Ansible tasks, write a YAML list of Ansible tasks as if they were written in a role.
You can include base Ansible tasks and Ansible modules for Dataiku.
Set Up Kubernetes and Spark-on-Kubernetes
You can set up Kubernetes (K8S) and Spark-on-Kubernetes for each instance linked to the template. If your Dataiku nodes connect to Kubernetes clusters, you must enable this setting.
Fleet Manager automatically downloads and configures the required packages and configurations to leverage Kubernetes clusters. This includes the Kubernetes plugin, the ability to attach container images, and define configurations for Kubernetes and Spark to point to the correct Azure Container Registry.
To do this:
Under Setup actions, choose Setup Kubernetes and Spark-on-Kubernetes.
To use the host IP instead of hostname for communication between pods and Dataiku:
Toggle Use private IP to On.
Remove a Setup Action¶
To remove a setup action from your instance template:
Launch Fleet Manager.
Under Settings, choose Instance templates.
Choose the instance template you want to modify.
Under Setup actions, delete the setup action you want to remove.
Select Save.
AWS Security¶
SSH Access¶
You can define the name of the AWS key pair to allow SSH access. Since Fleet Manager does not support multiple AWS accounts, this key pair must be defined in the same AWS account used to set up Fleet Manager.
To grant SSH access:
Navigate to AWS security > SSH access.
In AWS key pair name, provide a public SSH key.
This grants SSH access using the “centos” user which can run sudo commands. To authorize additional SSH keys, use the Setup action, “Add authorized SSH key.”
Instance IAM Role¶
There are two ways to grant your Dataiku instances access to AWS services: IAM roles and AWS access key.
It is a recommended best practice to use an IAM role and its instance profile rather than using an AWS access key. This IAM instance profile is auto-created when you create a role from the AWS console.
You can assign IAM roles to each instance linked to the instance template. The benefits of assigning IAM roles are:
Avoid unnecessary sharing of long-term access keys
Simpler to maintain than access keys
It is possible to have one role assigned at startup (before the Dataiku instance starts up) and another one at runtime (after the Dataiku instance starts up). This helps to limit the scope of the managed identity while the instance is running.
To assign Instance IAM roles:
Navigate to AWS security > Instance IAM role.
In Runtime instance profile ARN, provide the ARN (not a role ARN).
In Startup instance profile ARN, provide the ARN (not a role ARN).
Select the Restrict metadata access checkbox to prevent end-user processes from accessing the AWS metadata server.
This ensures the Dataiku end users cannot assume the instance role.
Keypair (Access Key)¶
You can use an AWS access key to access Dataiku.
If you prefer to use an AWS access key to access Dataiku (rather than using an IAM role), you’ll need to provide your ASM secret ID so that Fleet Manager can retrieve the secret access key from AWS Secrets Manager (ASM). Alternatively, Fleet Manager can encrypt it and store it, using your Customer Manager Key (CMK) defined in the cloud setup settings.
To assign an AWS access key:
Navigate to AWS security > Keypair.
In Keypair mode, choose AWS Keypair.
In Keypair storage mode, choose an option.
Secret stored in ASM.
Enter your ASM secret id.
Enter your AWS access key id.
Secret stored encrypted in Fleet Manager.
Enter your AWS access key id.
Enter your AWS secret access key.
License Override¶
You can use the license override setting to apply a Dataiku license file to each instance linked to the template. Alternatively, you can specify a license file for each instance.
Navigate to License override (Optional) in the template.
In License file, select Enter License.
Enter your license file. Be sure to copy the entire contents of the JSON file, including the final ‘}’.
Fleet Manager agent will apply the license file to each instance linked to the template once you have saved your changes and reprovisioned each instance.
To update a license file, repeat these steps.
Creating or Modifying a Virtual Network¶
A virtual network defines where Dataiku instances are deployed. A virtual network represents the network context in which instances are launched. It is a reference to the virtual network provided by your cloud provider. It contains configuration information, including how DNS and HTTPS are handled.
You can create a new virtual network or choose to modify an existing one. If creating a new virtual network, Fleet Manager automatically completes the VPC and subnet fields based on the VPC and subnet where the Fleet Manager is currently running.
Note
Instance templates are not tied to a specific virtual network. However, Dataiku instances are tied to a specific virtual network. Once a virtual network is associated with an instance, you cannot change to a different virtual network.
To view a virtual network:
Launch Fleet Manager.
Under Settings, choose Virtual networks.
Choose the virtual network you want to modify.
Fleet Manager displays the virtual network’s dashboard.

To modify a virtual network:
Select the Settings tab.
Modify the settings according to the guidelines and then select Save.
Virtual Network Guidelines¶
Virtual Network Name¶
When creating a new virtual network, Fleet manager asks for the virtual network label. When you deploy Dataiku instance(s) from a Fleet Manager blueprint, the virtual network is pre-configured with the fleet’s name.
To edit the virtual network name:
In Label, enter a name for the virtual network.
Assign a Public IP Address¶
You can assign a public IP address to all Dataiku instances linked to the virtual network.
To do this:
Select the Assign a public IP address checkbox.
Security Groups¶
Default Security Groups
Fleet Manager automatically creates AWS security groups for all Dataiku nodes linked to the virtual network. This is the default configuration.
To automatically create security groups when creating a new virtual network:
Toggle Auto-create security groups to On.
The default security group configuration permits the following:
DSS nodes to be reached from 0.0.0.0/0 on ports 80, 22, and 443.
DSS nodes to communicate with each other.
Fleet Manager to communicate with Dataiku nodes if you choose to deploy nodes in another VPC/subnet from Fleet Manager.
If you choose not to automatically create AWS security groups, you can attach your own custom security groups.
Custom Security Groups
To attach your own security groups:
Toggle Auto-create security groups to Off.
Select Add Security Group.
In Security groups Ids, enter the id of each security group, separated by a comma.
Fleet Management¶
You can enable Fleet Management so that all the instances linked to the virtual network know each other. This simplifies the configuration of log centralization and of the deployer.
To enable Fleet Management configuration options:
Select the Enable checkbox.
Event Server
You can specify the address of the event server. This is a Dataiku node that is enabled to collect audit logs from other Dataiku nodes linked to the same template. This allows you to centralize the logs in a single location.
To do this:
In Event Server, enter the name of the node that should act as the centralized event server for logs concentration.
Fleet Manager will send all audit logs for all nodes to this node.
Deployer Management
Select a Deployer strategy.
Do not manage deployer.
Central deployer. Select this strategy if you have more than one Design node or you may have more than one Design node in the future. As a result:
The Deployer is deployed as a standalone node and all other nodes are configured to connect to it.
Deploy from design nodes. Select this strategy if you have a single Design node and want a simpler setup. As a result:
Your Design node is enabled as a Deployer node, and
Every Automation node is configured as a deployment infrastructure in the Deployer.
Govern Server
You can define your Govern node so that it is automatically configured in all Dataiku nodes linked to the virtual network.
In Govern Server, enter the node’s ID (the instance name as defined in Fleet Manager) that should act as the centralized Govern server.
DNS Strategy¶
If you manage your DNS zone in Route53 in the same AWS account where you deployed Fleet Manager, you can have Fleet Manager create the DNS entries to define the vanity URLs for the Dataiku instances. Fleet Manager will use the instance name (nodeID) that was associated with the Dataiku instance at deploy time to create a DNS entry that associates the IP address of the instance to the DNS name. This requires the role associated with Fleet Manager to have the required policies to manage Route53.
To do this:
In DNS strategy, choose Assign a Route53 domain name that you manage.
Enter the Zone Id in Route53 Zone Id for private IP if available.
Enter the Zone Id in Route53 Zone Id for public IP.
SSL Strategy¶
You can manage the TLS certificates associated with each Dataiku instance linked to the virtual network.
In HTTPS strategy, choose a strategy:
None (HTTP) only. Does not manage TLS at all. The Dataiku instance is only accessible via the HTTP (80) port.
Self-signed certificates. Each Dataiku instance will have a self-signed certificate created automatically.
Enter a certificate/key for each instance. Select this strategy if you prefer to manage the certificates yourself. You’ll need to specify a certificate and key per each instance in the instance’s settings.
Generate certificates using Let’s Encrypt. This strategy leverages “Let’s Encrypt” to generate certificates for each instance. “Let’s Encrypt” needs to be able to complete the DNS challenge to create a certificate. To allow this, you’ll need to configure the Route53 Zone Id for public IP in the DNS strategy. This strategy automatically renews the certificate before it expires.
Enter an email address in Contact Mail.
In HTTP strategy, choose a strategy:
HTTP port is disabled.
HTTP port redirects to HTTPs. This is the recommended option.
When modifying a virtual network template or creating a new network template, Fleet Manager deploys the virtual network in AWS.
Applying the Modifications¶
Fleet Manager lets you know when modifications require reprovisioning before the changes take effect.
To reprovision an instance:
From Instances, choose All and then locate the instance you want to reprovision.
Select Reprovision.
Select Confirm.
Wait while Fleet Manager reprovisions the instance.