Concept Summary: Architecture Model for Databases¶
In the previous video, you learned about SQL datasets in Dataiku DSS, how these datasets are created, and some of their attributes. Let’s now summarize the key points of the video before continuing on to the next lesson.
Database Integration¶

By integrating with data sources, such as the SQL databases in the previous figure, DSS is able to directly read from a database, write to a database, and process data using a dedicated database engine.
Importing a Dataset¶
Dataiku DSS allows you to import a dataset through an existing SQL connection by selecting the table that you want to import from a list of the tables in the database, and then creating the dataset.
Writing to a Database¶
You can directly write data from DSS to an SQL database by using any visual recipe, for example, a Sync recipe or a Prepare recipe. You can also write to an SQL database by using certain code recipes, such as a Python recipe or an R recipe.
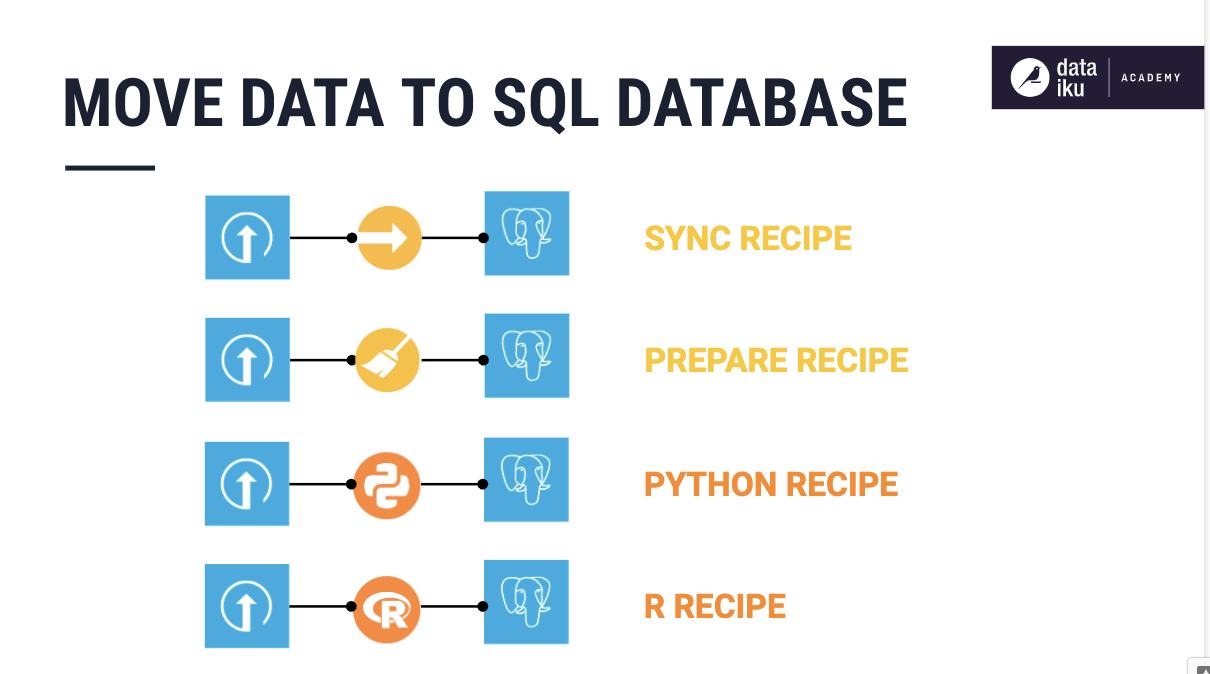
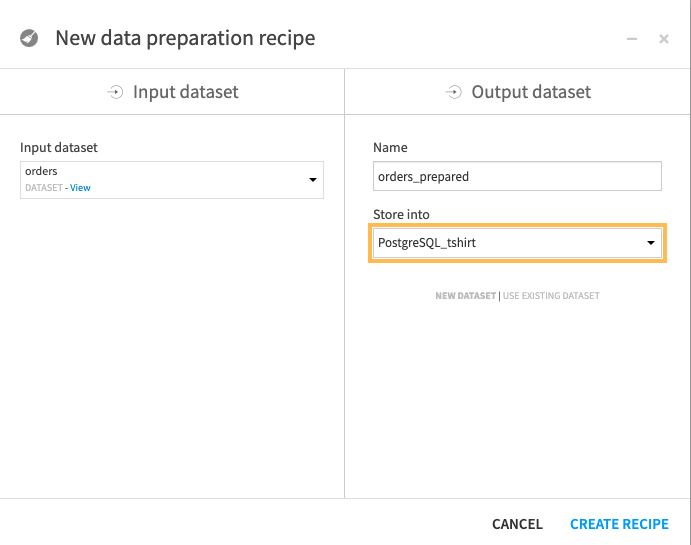
When creating the recipes, specify the database as the storage location of the output tables, by using a connection, such as a PostgreSQL connection.
Note
SQL datasets in DSS are pointers to database tables. Therefore, the data is only written in the SQL database. Database concepts of rows, columns, and column storage types also apply to the SQL datasets.
Database Connection Settings¶
The settings of the SQL connection determine the database and schema where the tables are created. DSS also sets the names of the database tables by adding a prefix to the names of the datasets in DSS.
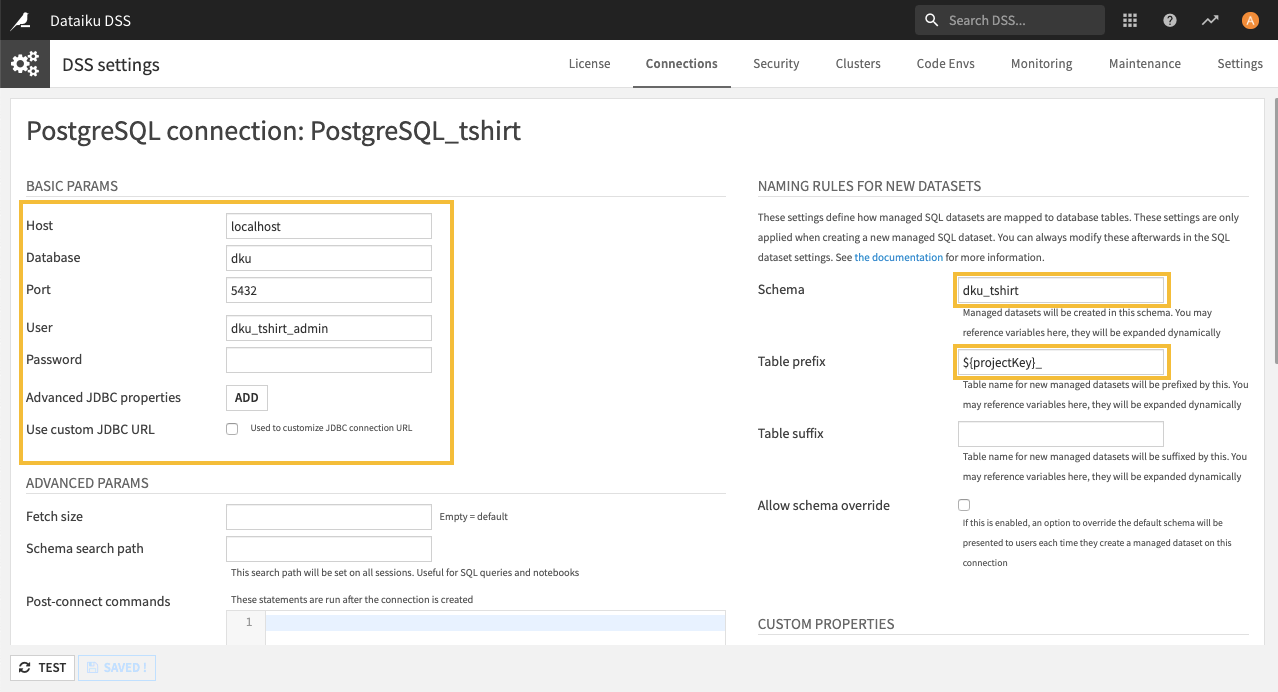
Finally, DSS sets the column types, so that you don’t have to write CREATE TABLE statements.
For more information, see SQL databases in the product documentation.