Working with MongoDB in DSS¶
MongoDB has become very popular over the past years, and may be encountered in many industries and projects. We will show in this article how to read and write data to MongoDB from DSS.
Technical Requirements¶
You have access to a MongoDB instance with an existing database and collections. Here, we have a local MongoDB instance, with a “dataiku” database and a “github” collection. The collection uses data from the GitHub Archive, which is a project to record the public GitHub timeline, archive it, and make it easily accessible for further analysis. The raw data is provided as JSON, which makes it perfectly suitable for MongoDB.
Create the MongoDB connection¶
If you use a MongoDB data source, the first thing to do in DSS is to create the corresponding connection. In the Administration menu of DSS, under the Connections tab, click on “New connection” and select “MongoDB”:
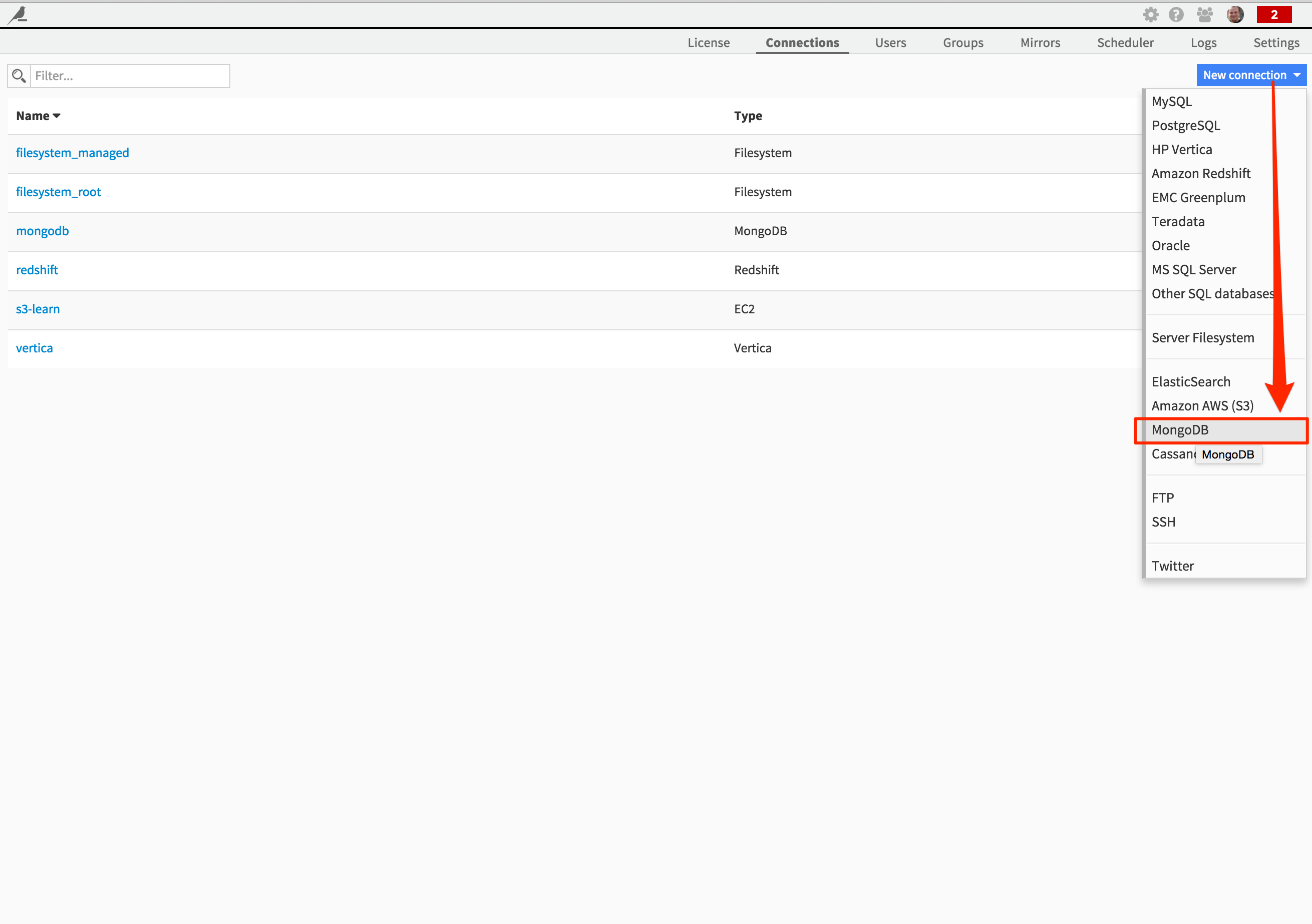
Fill in the connection credentials as required:
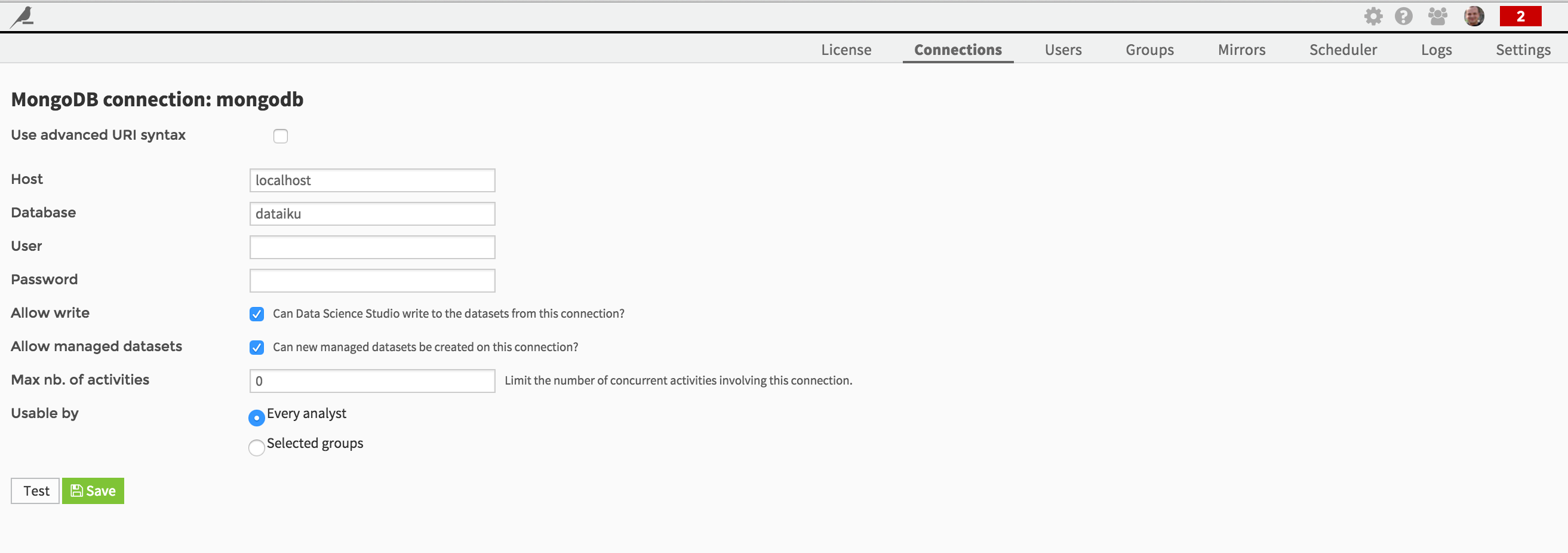
Note that you are able if needed to define the connection using an advanced URI syntax.
Create a MongoDB dataset¶
Once your connection created, you can easily access to the data stored there by creating a new MongoDB DSS dataset (from the Dataset > New menu). Just browse the collections and select the one you want to use as dataset:
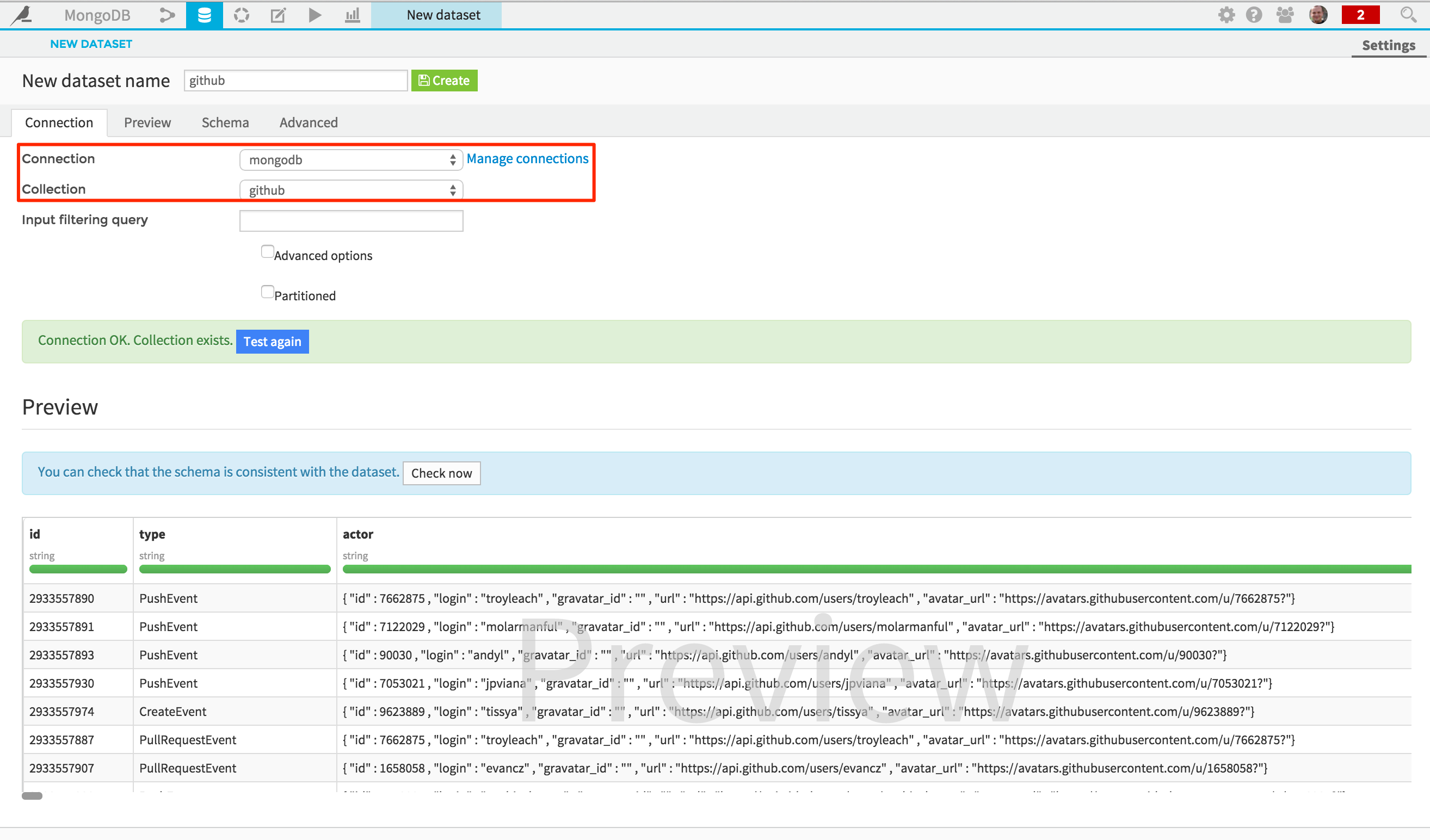
Note that you can also limit the results returned by using the “Input filtering query” field:
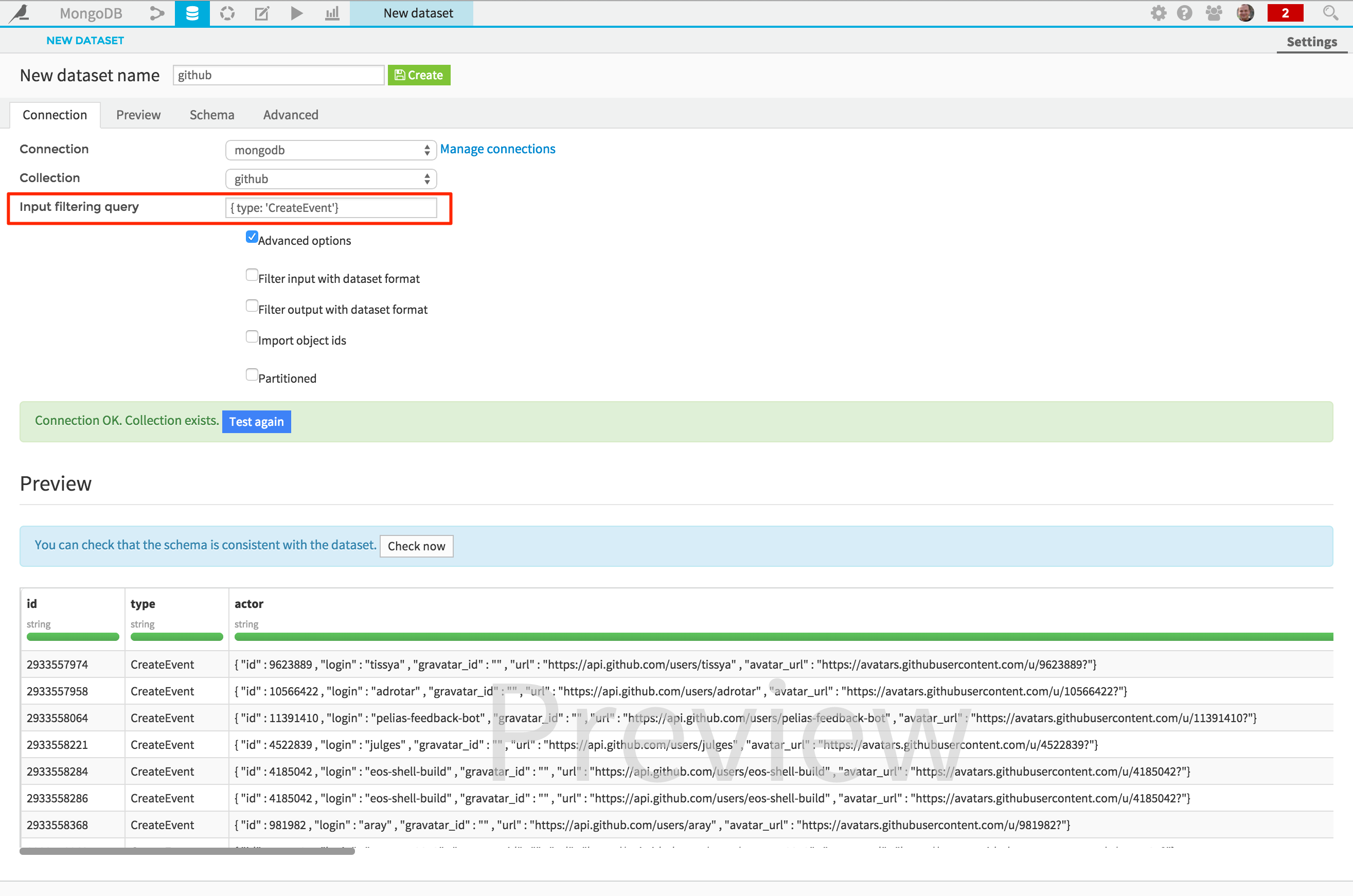
Analyze your data¶
You are now ready to analyze your MongoDB data. For instance, you could use a visual data preparation script from “Analyze” to flatten or unfold the documents stored in your MongoDB collection:
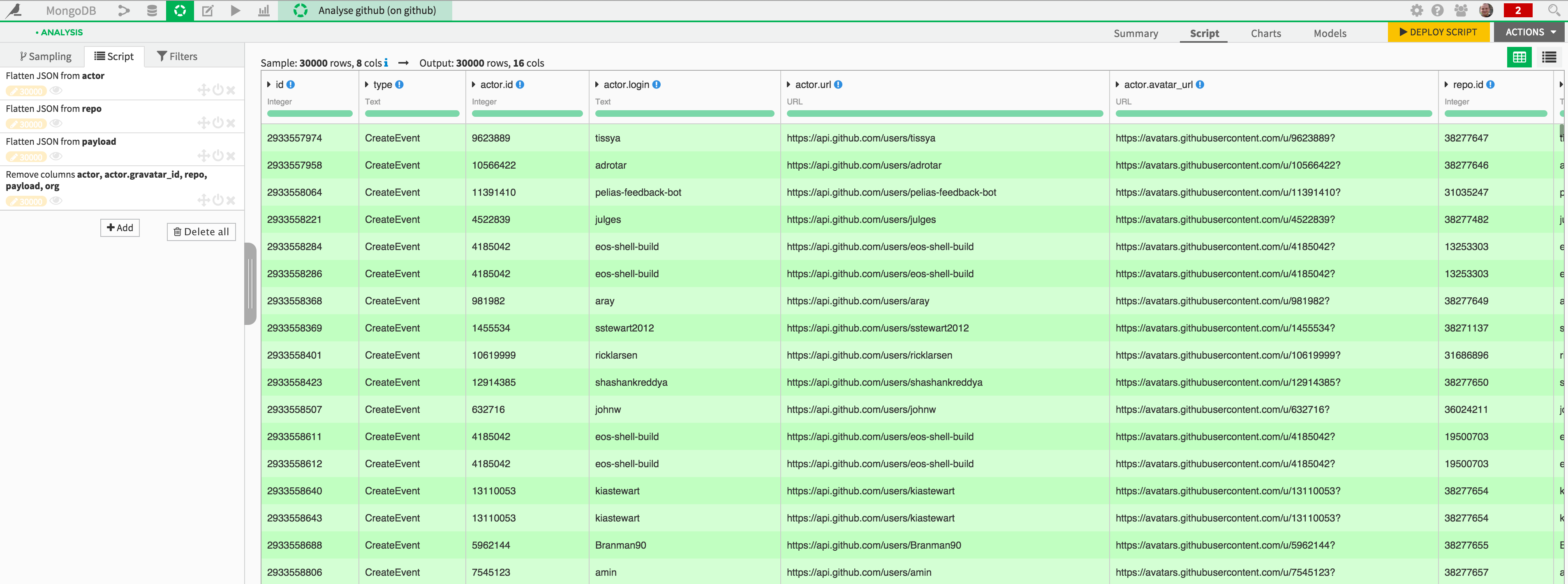
You may also write the data to MongoDB, for instance if you wished to expose it in a web-based application. Suppose the following dataset has been built:
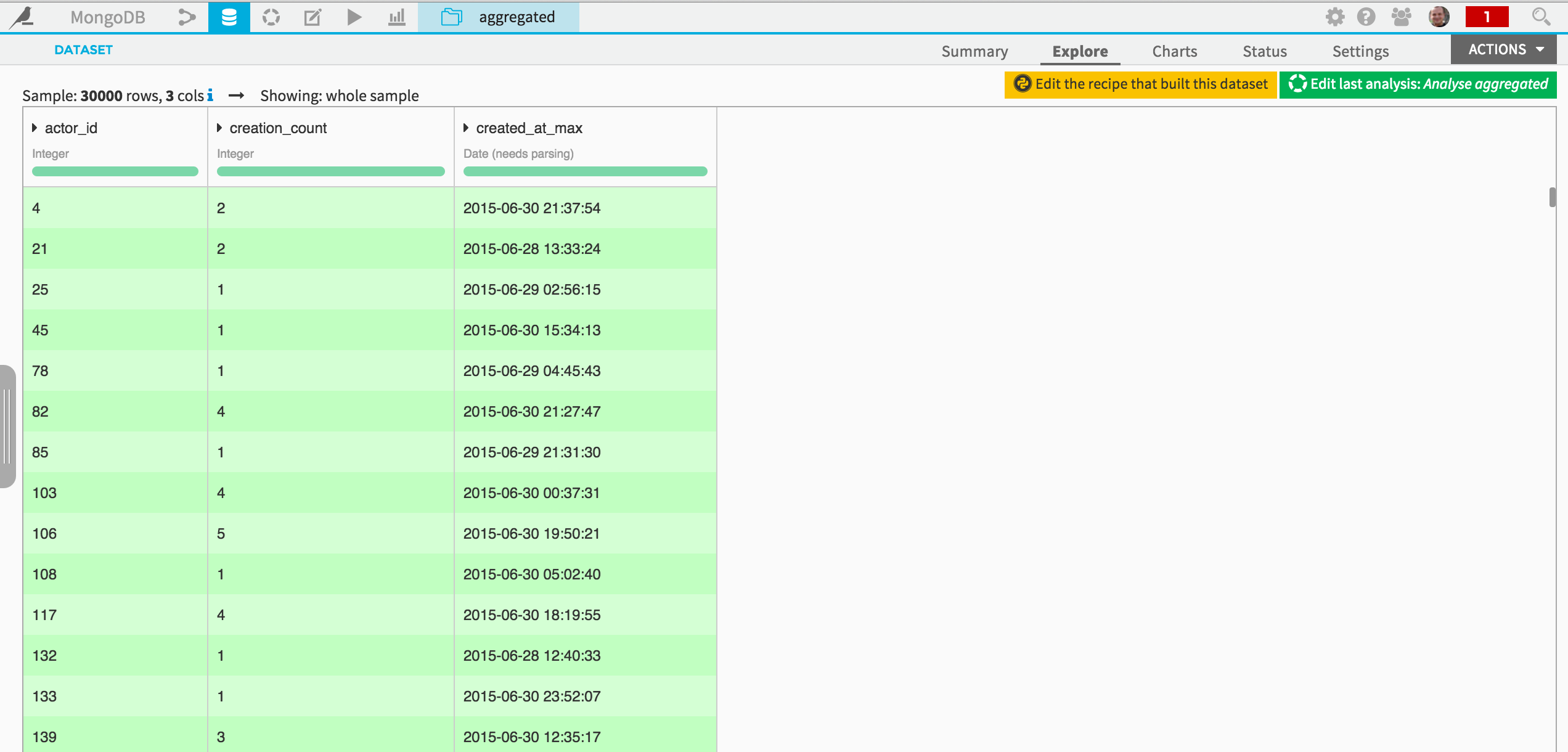
You could then use a visual preparation script to create a document from each record, using a custom Python formula, for instance:
import json
def process(row):
return {
'actor_id': row['actor_id'],
'stats': [
{'creation_count': int(row['creation_count'])},
{'created_at_max': str(row['created_at_max'])}
]
}
Finally, you could write this data to MongoDB by deploying the script, and specifying your MongoDB connection as target:
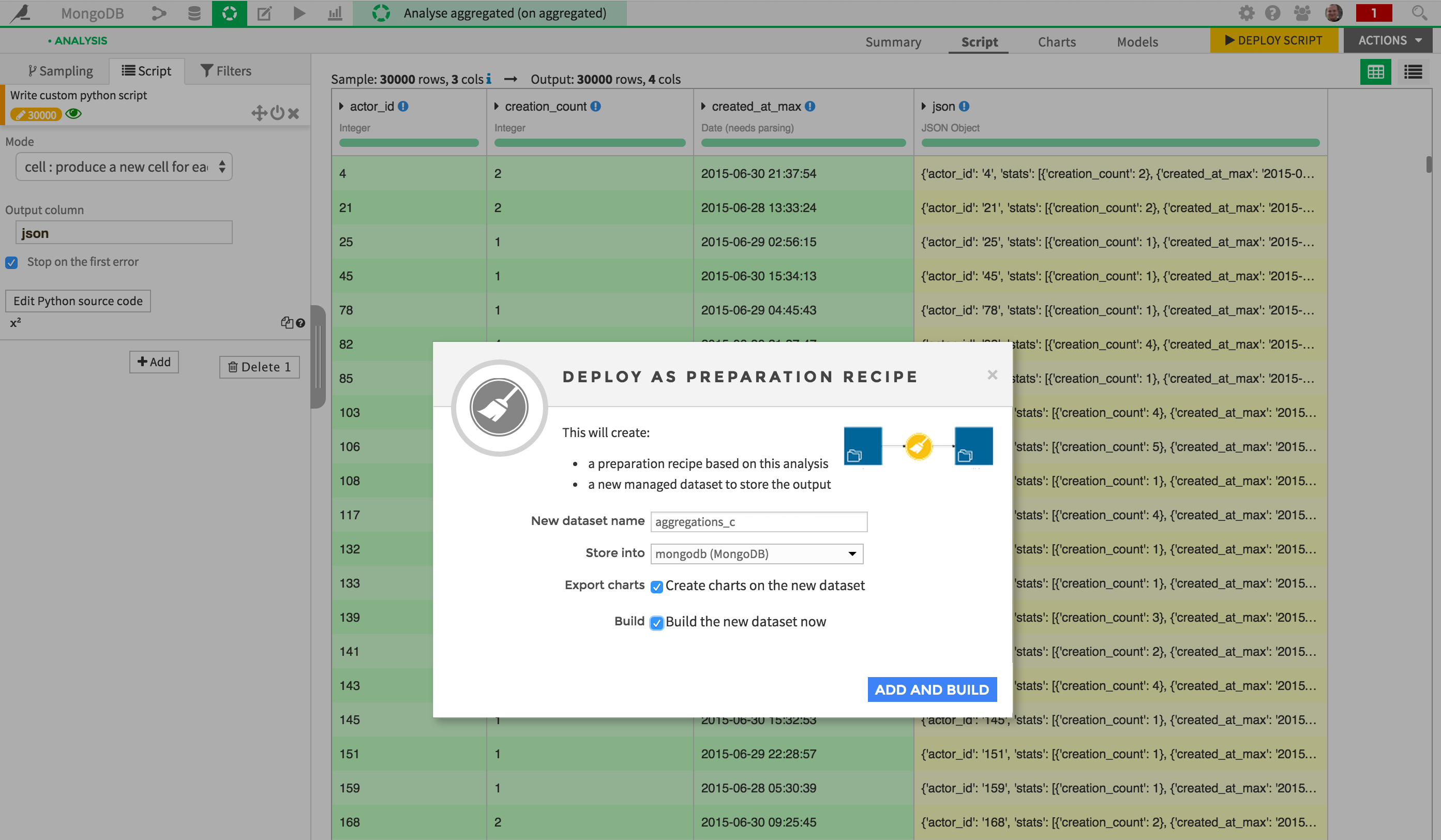
Wait for your script to run. Your data is written into a new MongoDB collection. You may want to check the output directly from a Mongo shell to be sure it worked:
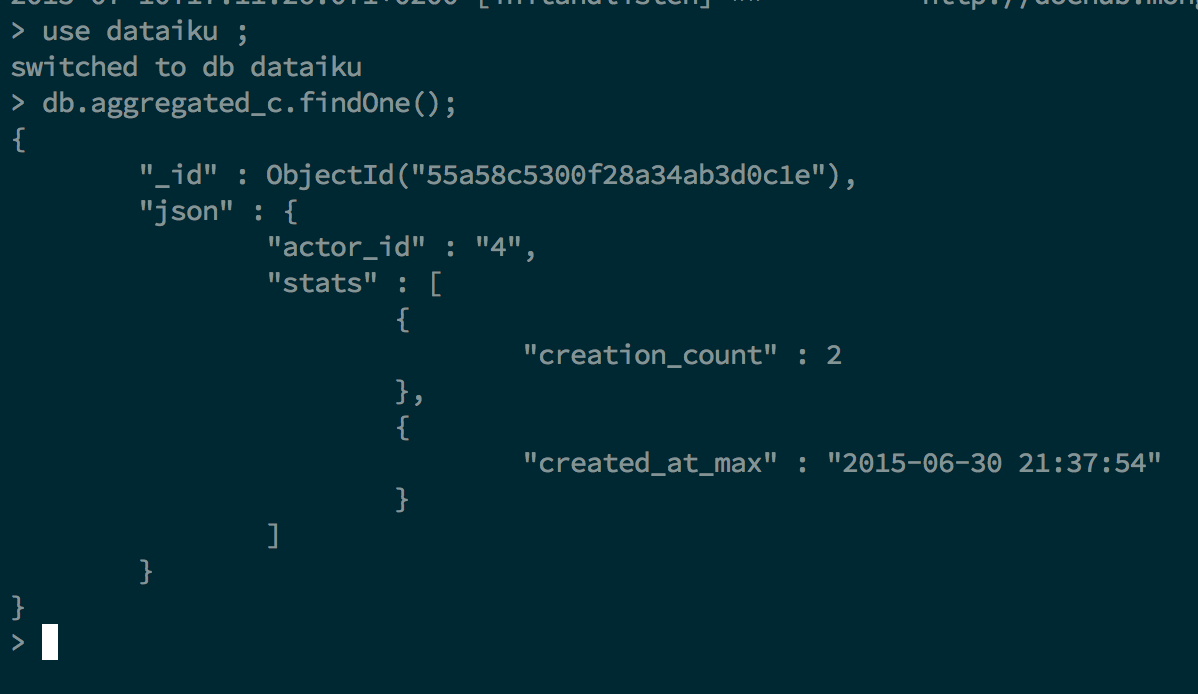
That’s it for a first taste of integrating DSS and MongoDB.