Concept | Dataiku APIs#
Watch the video

In this article, you will learn about APIs in Dataiku.
The value of APIs#
Your first introduction to Dataiku may have been through its visual representations of datasets, recipes, and models.
For many use cases, these visual, point-and-click tools can quickly get the job done, while also opening avenues for collaboration with a much broader set of colleagues.
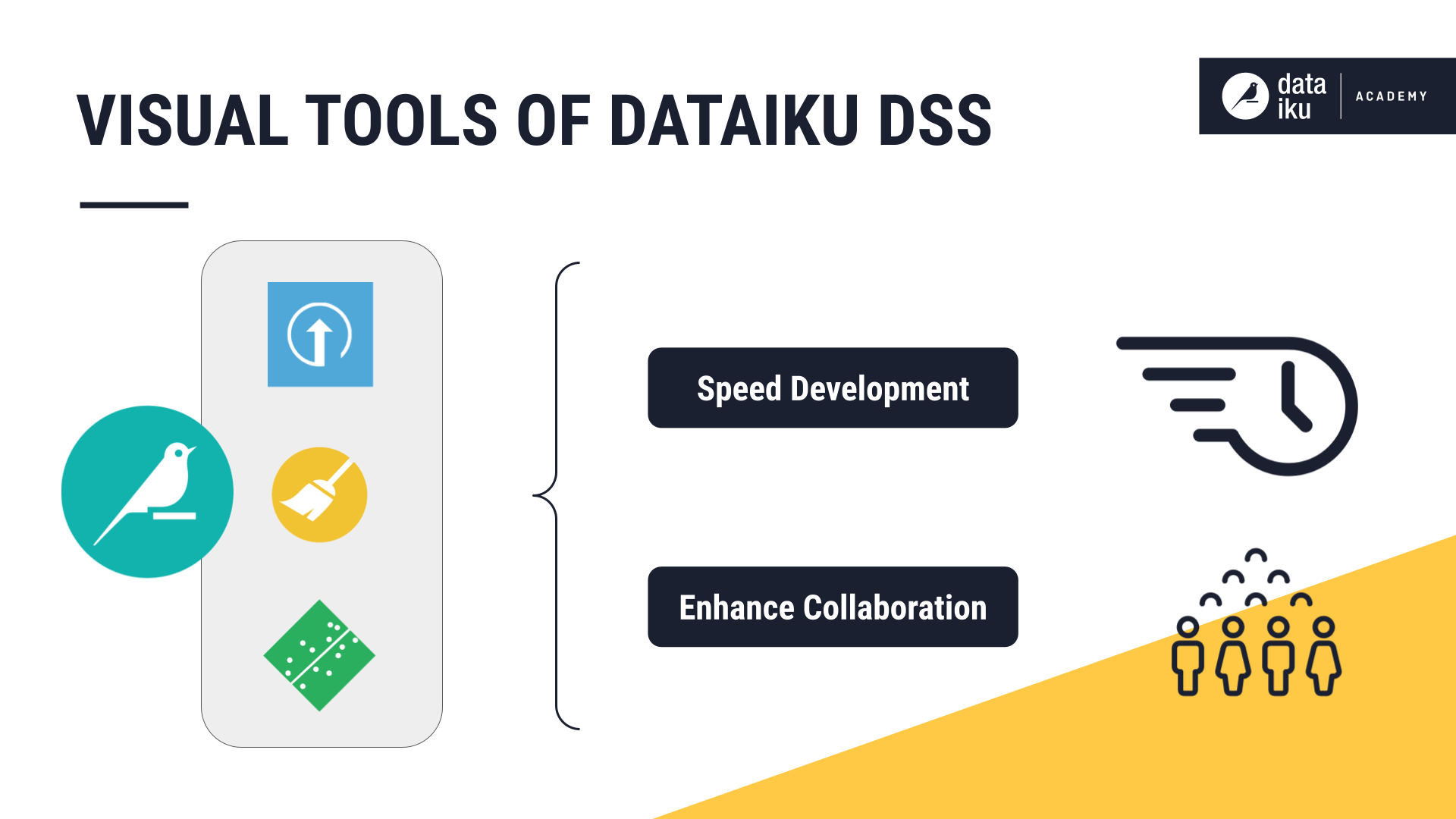
As a developer, you don’t want a visual interface to limit what you can do. Dataiku provides APIs that let you interact programmatically with Dataiku objects and the platform itself—so you can work entirely in code when needed.
The APIs provide coders the flexibility to accomplish the same tasks offered by the visual interface (and much more) by writing code.
Note
While examples often use Python (dataiku), similar functionalities are available as a REST API, for R, and other supported languages.
Working with the Dataiku API#
The Dataiku API gives you programmatic access to your instance, projects, and the objects within them. You can leverage the API inside Dataiku (in code recipes, notebooks), code studio , webapp, scenario, and many more, or outside Dataiku (from your own IDE or an orchestration tool).
With the API, you can perform two broad categories of actions:
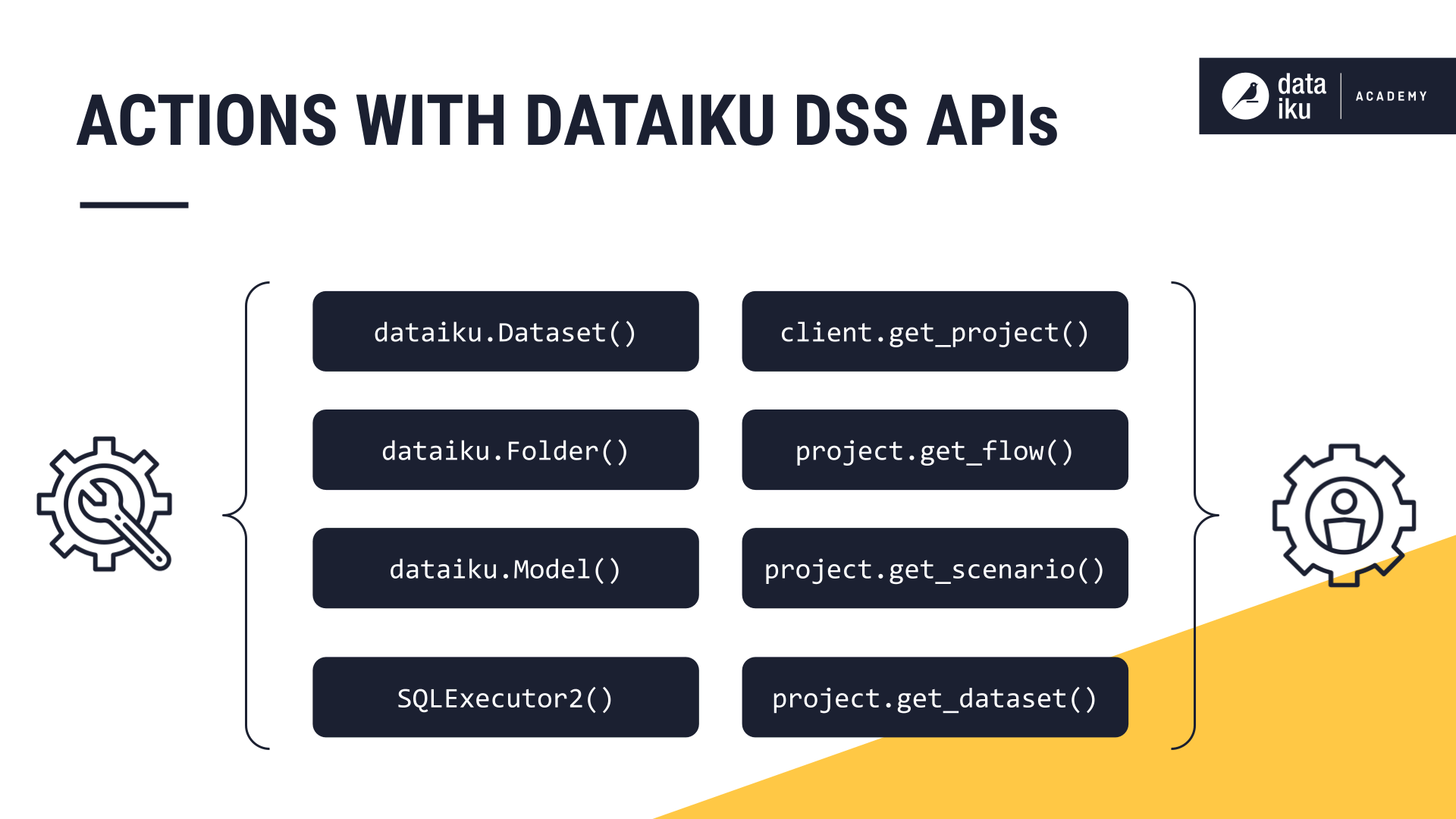
Instance and project operations: Create and manage projects, groups, and users; build Flows; check the status of jobs and scenarios.
Object-level operations: Read from and write to datasets, interact with folders and saved models, or perform dynamic SQL queries.
Inside Dataiku#
When working inside Dataiku, the API handles the low-level engineering needed to connect to datasets, folders, and other objects. Within a code recipe or notebook, the API package is automatically available, so you can start coding without any explicit installation.
Typical examples include:
Reading from or writing to datasets.
Interacting with folders and saved models.
Running dynamic SQL queries.
See also
To get started, see Getting started in the Developer Guide.
For the full list of methods and classes, see the API Reference.
Outside Dataiku#
The API also extends beyond the platform. From your own IDE, a remote script, or an orchestration tool, you can use the API to interact with your instance programmatically.
Tip
To get started externally, install the dataikuapi package and set up authentication.
For detailed instructions, see the tutorials of the Developer Guide.
This is especially useful for:
External orchestration: Run scenarios and automate tasks from a third-party scheduler.
Custom applications: Build services or webapps that connect to Dataiku.
Remote administration: Manage projects, users, and permissions outside of the UI.
Under the hood, these calls are served by a REST API. However, it’s recommended to access them through the Python client package dataikuapi, which makes the API easier to use in code.
Key use cases#
The API allows you to perform a wide range of tasks, from simple project-level actions to complex instance-wide administration. Here are some common examples:
Use case |
Examples |
Learn more |
|---|---|---|
Automate project tasks |
Run scenarios, rebuild datasets, or trigger Flow runs on a schedule. |
|
Administer Dataiku remotely |
Manage users, groups, and permissions; monitor project and job status; configure connections and project settings. |
|
Integrate with other systems |
Trigger Dataiku jobs or pipelines from external orchestrators (for example Airflow), or pull data from Dataiku into custom scripts or applications. |
|
Deploy and manage services |
Upload project bundles from a Design node to an Automation node, or manage API service packages on API nodes. |
See also
For more tutorials and code examples for each of these use cases, browse the Developer Guide tutorials.
Next steps#
Now that you have a conceptual understanding of the Dataiku API, the best way to learn is by practicing. For hands-on tutorials and code-based exercises, you’ll find relevant materials on the Developer Guide.
Get started with the API: Follow the getting started tutorials to set up your environment and make your first API calls.
Automate tasks: Learn how to trigger scenarios or update datasets.
Explore more: Browse the full API Reference for all available methods and classes.