Concept | Build modes#
Watch the video

Datasets in Dataiku often have dependencies on upstream datasets in the Flow. As a result, these downstream datasets can become outdated if users make changes to preceding datasets or recipes.
Dataiku offers many build methods to counter or prevent issues that may arise from these dependencies. But why so many options? Once you start scaling datasets, you won’t want to run any unnecessary computation. This article outlines different build strategies that will help you build exactly what you need.
Note
You can apply the same strategies to building other objects in Dataiku like models and model evaluation stores.
Build modes#
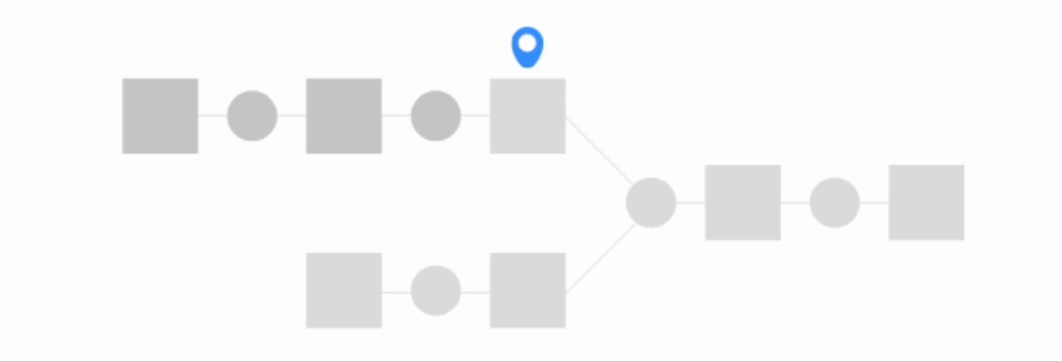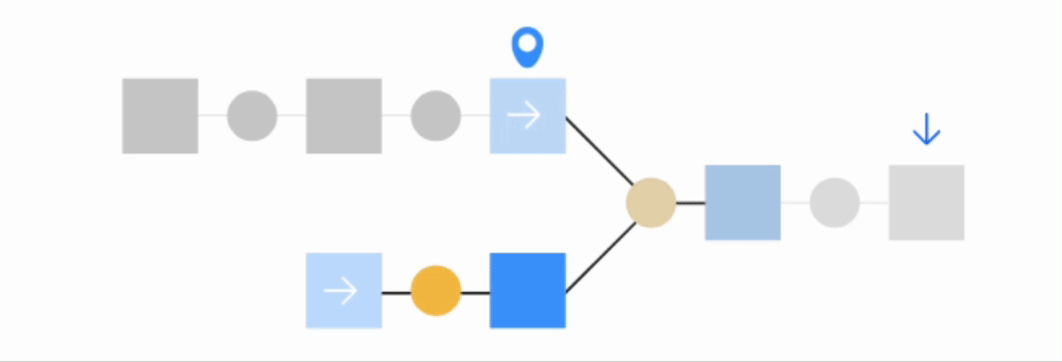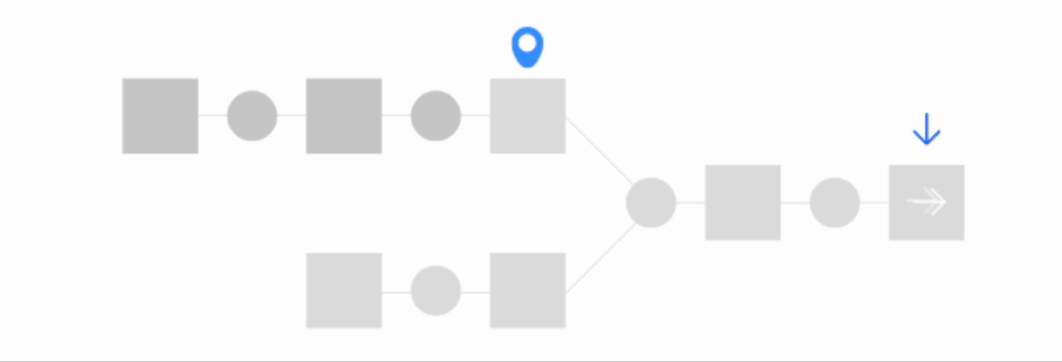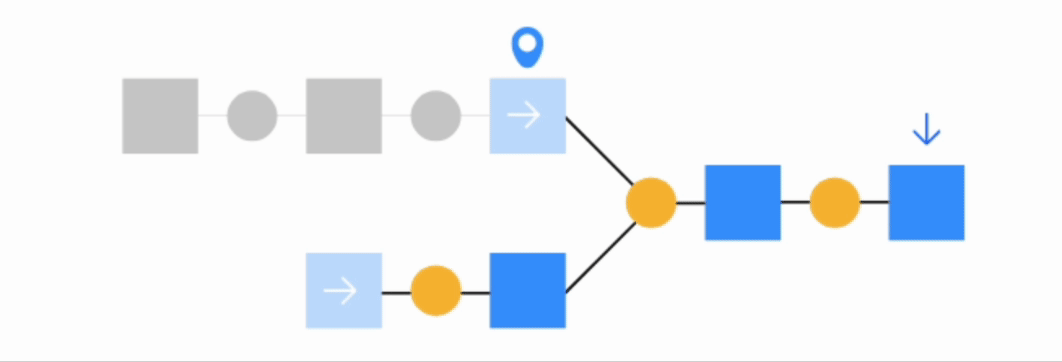
There are three main build modes to consider when building datasets in Dataiku.
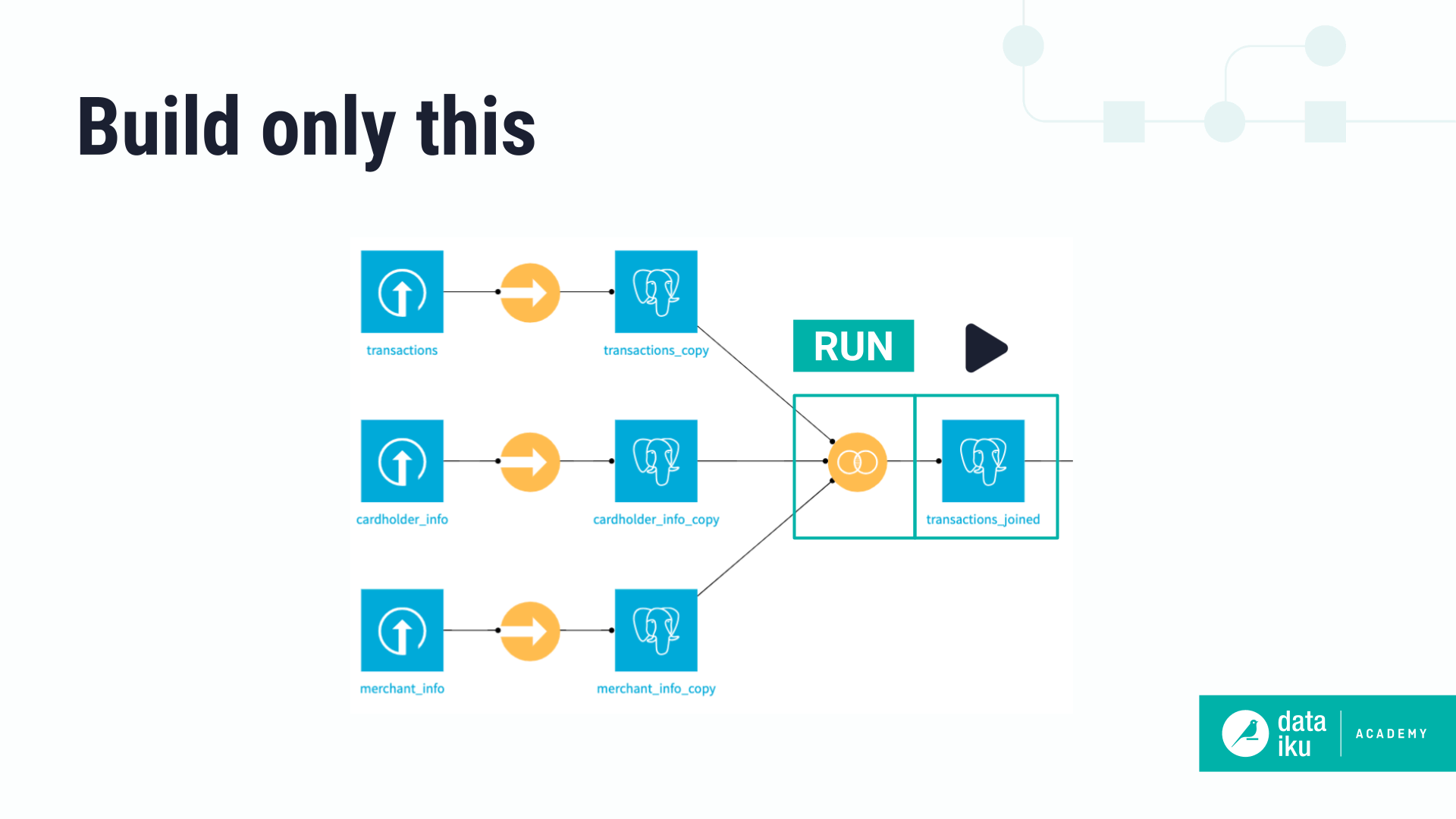
Build only this#
The simplest way to build a dataset is by using the Build only this option. This is the default build option for all datasets aside from those at the beginning of the Flow. It only runs the specific recipe that outputs the dataset.
Build upstream#
The Build upstream option builds the selected dataset and upstream datasets. There are two types of upstream builds:
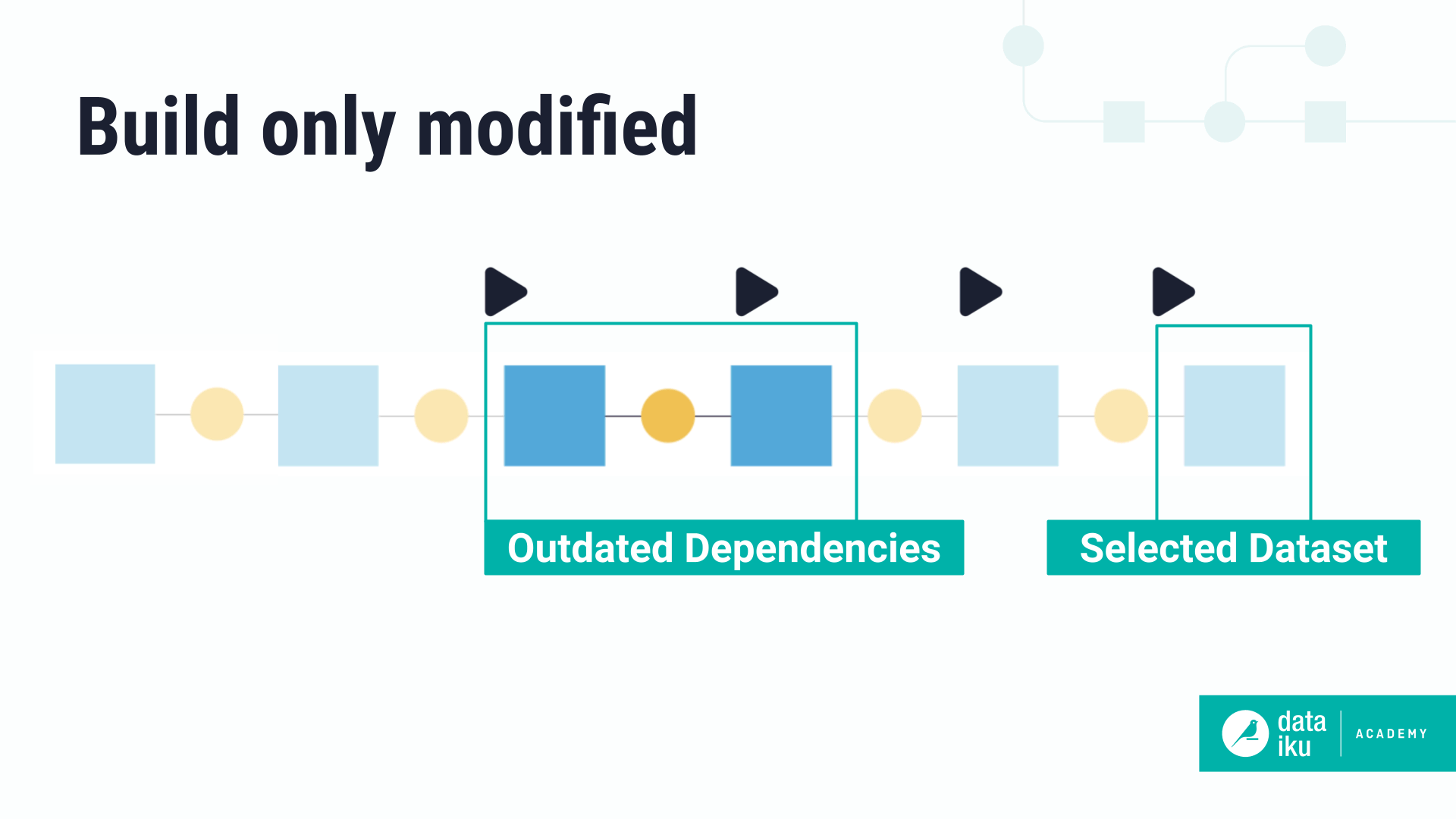
Build only modified#
This option will only build upstream datasets starting from the first outdated dataset. This way, you won’t have to rebuild the entire branch.
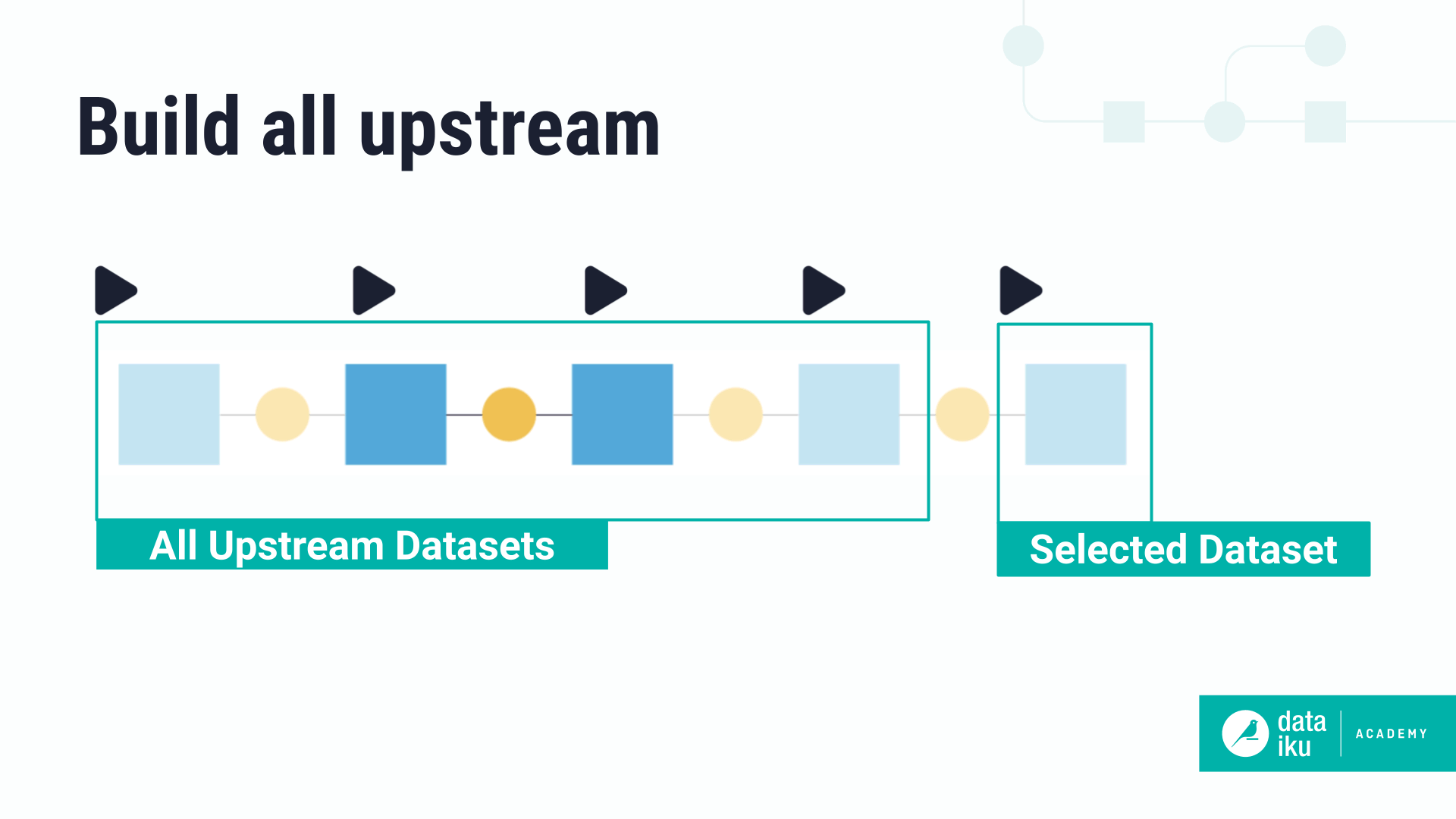
Build all upstream#
This option rebuilds all upstream datasets, regardless of if they’re already up-to-date.
Tip
You can also choose to build upstream and Stop at zone boundary. This means that upstream dependencies located outside the Flow zone won’t be rebuilt even if they’re outdated.
Build downstream#
The Build downstream option builds downstream datasets. Let’s look at the Advanced settings.
Build all downstream#
This option runs recipes from the selected dataset until reaching the end of the Flow. The selected dataset itself isn’t built.
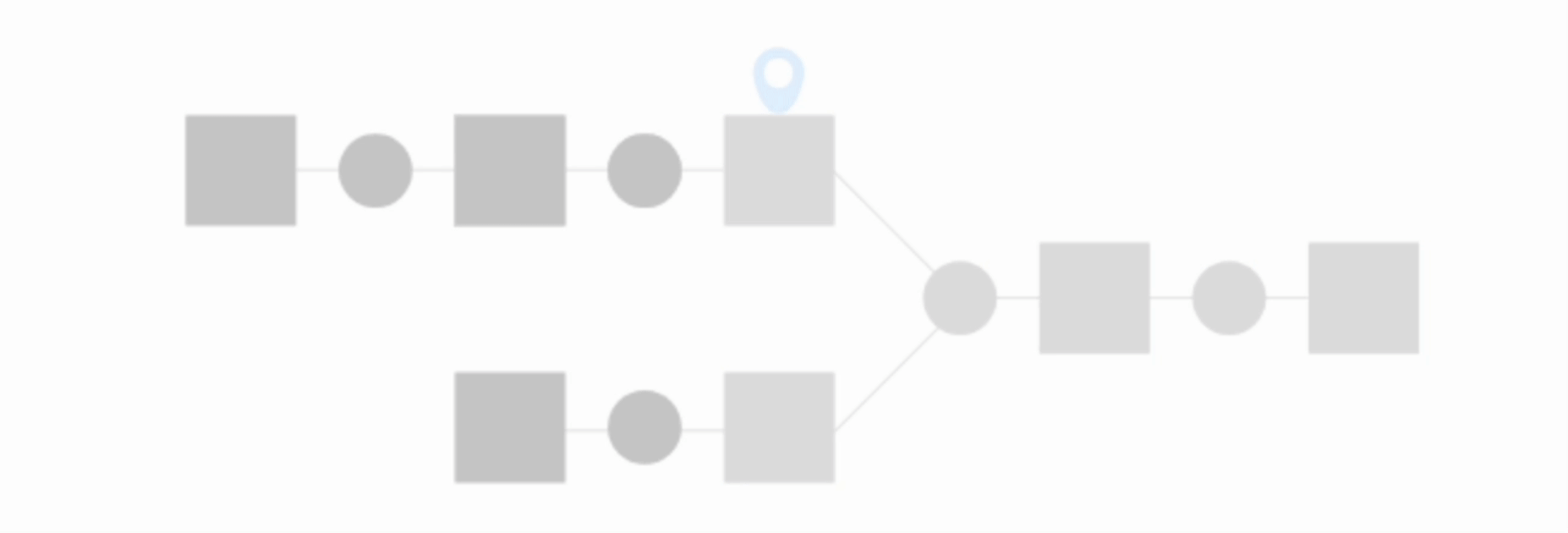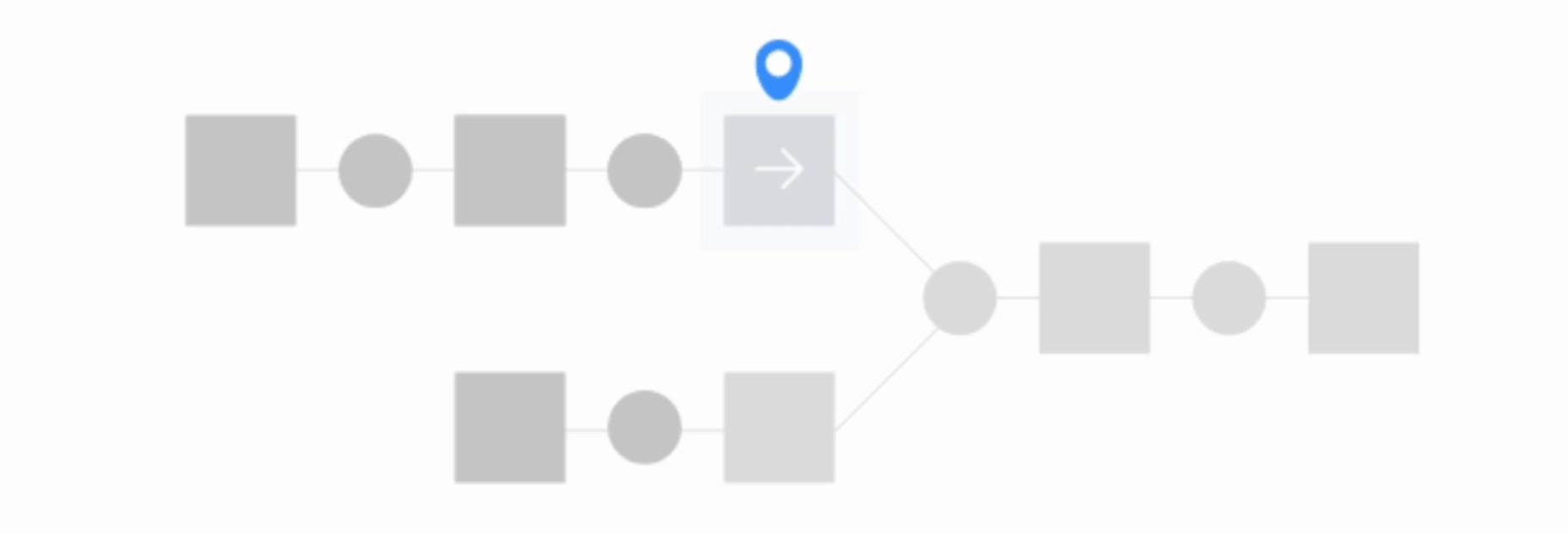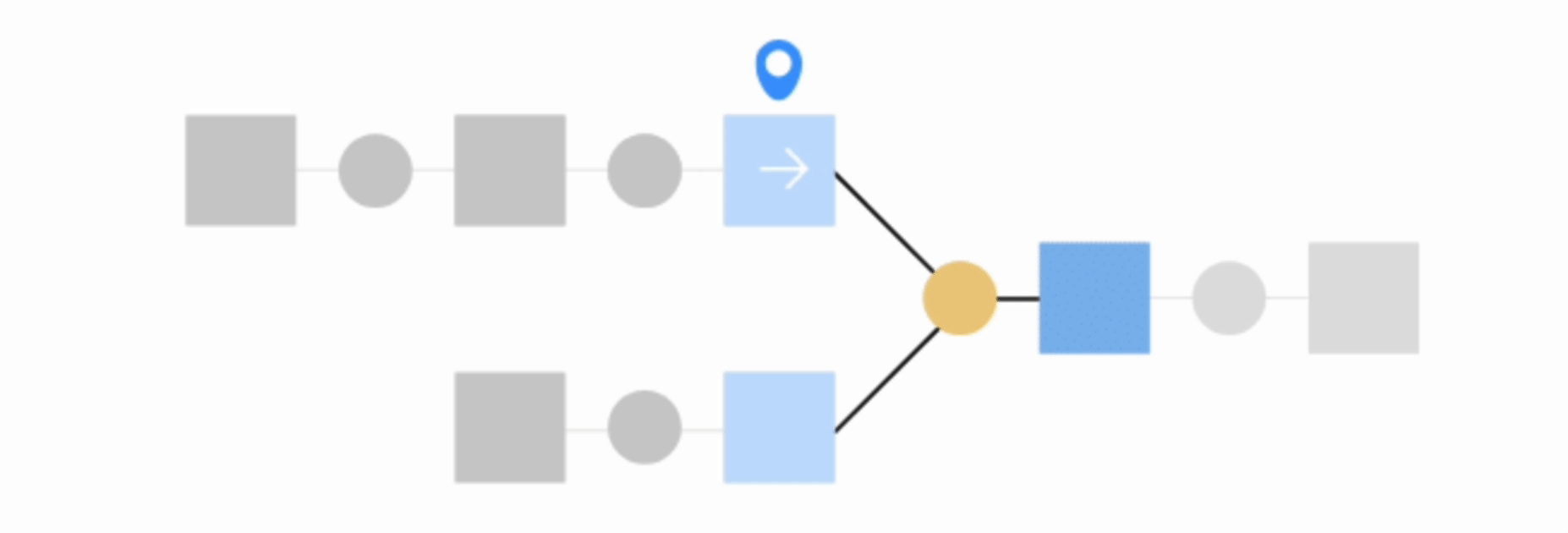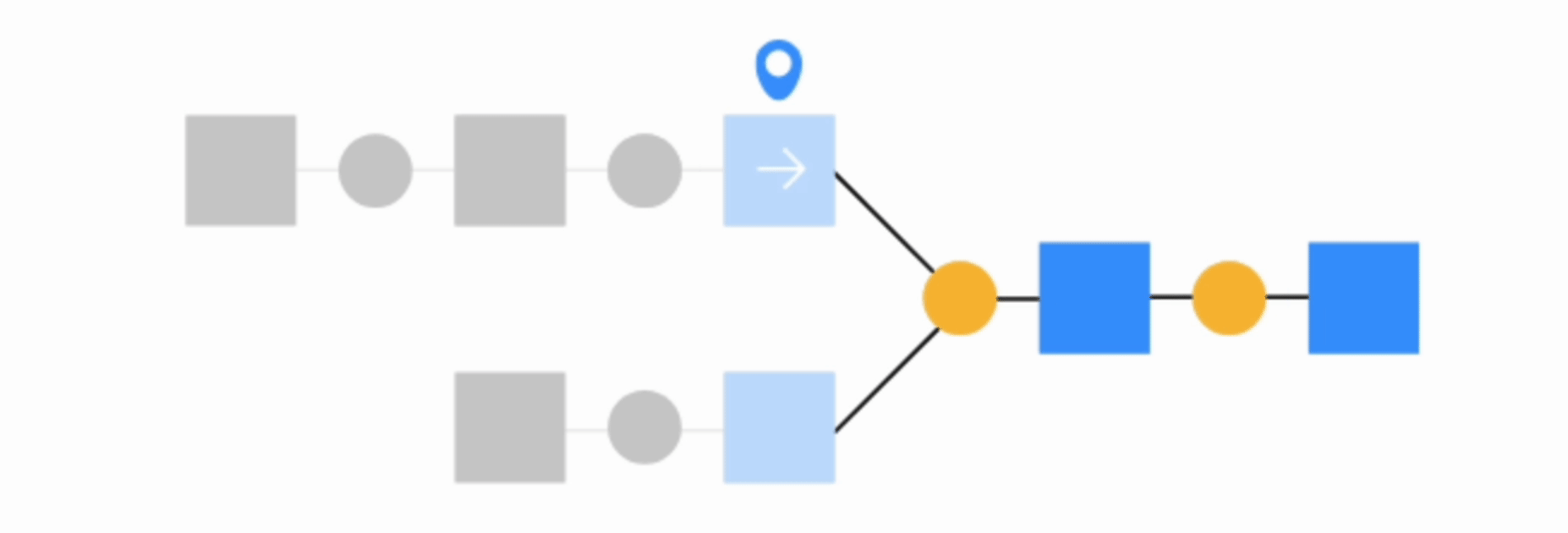
Find outputs and build recursively#
This option will make Dataiku find all final datasets downstream from selected dataset and build any upstream dependencies. In this case, you can choose to either build required dependencies or force-build those upstream datasets.
Update output schemas#
A schema describes the structure of a dataset. It includes the list of columns and their respective names and storage types. Often, the schema of datasets will change when designing the Flow. Dataiku provides a way to ensure that schema changes are correctly applied to downstream datasets.
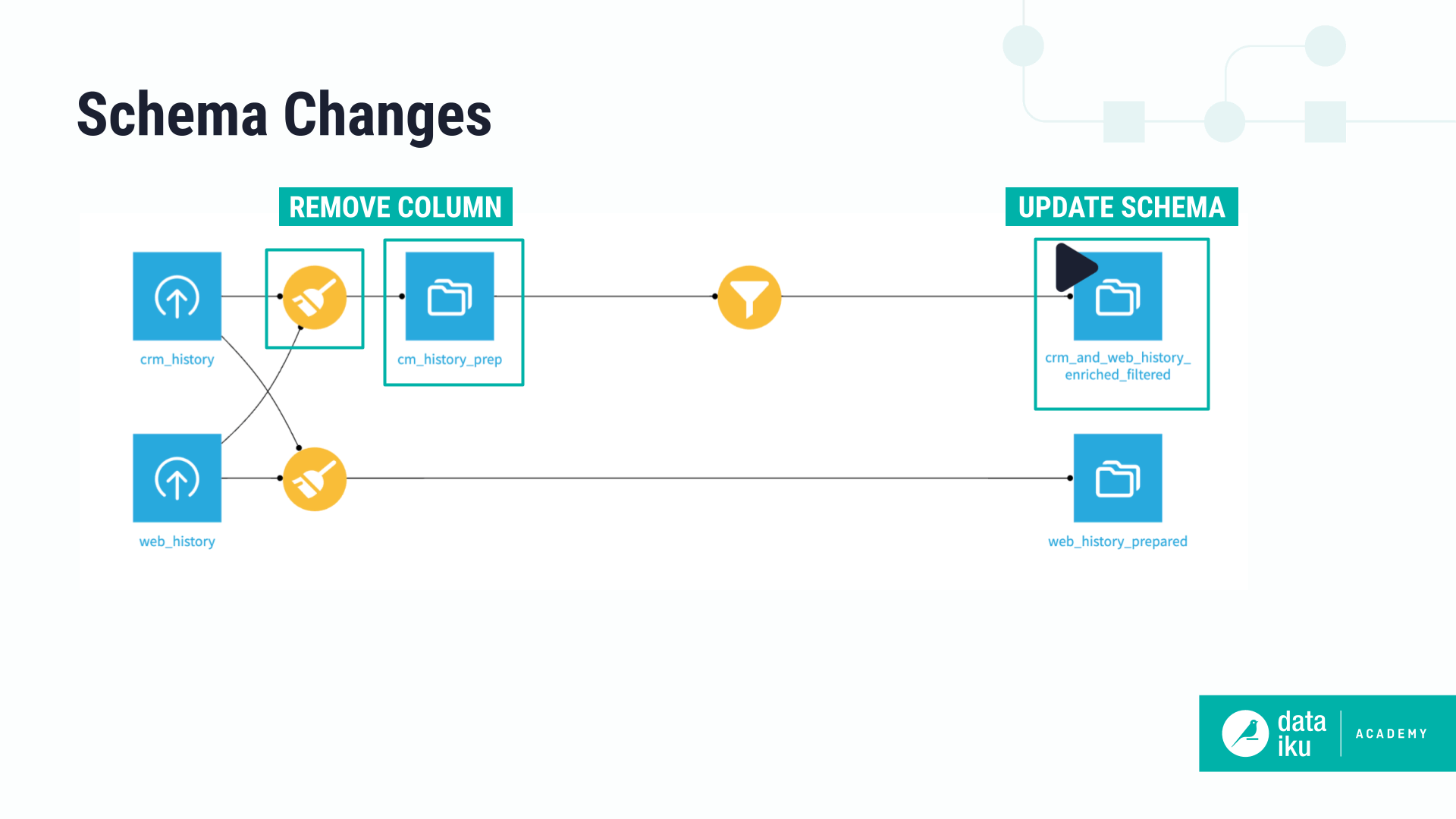
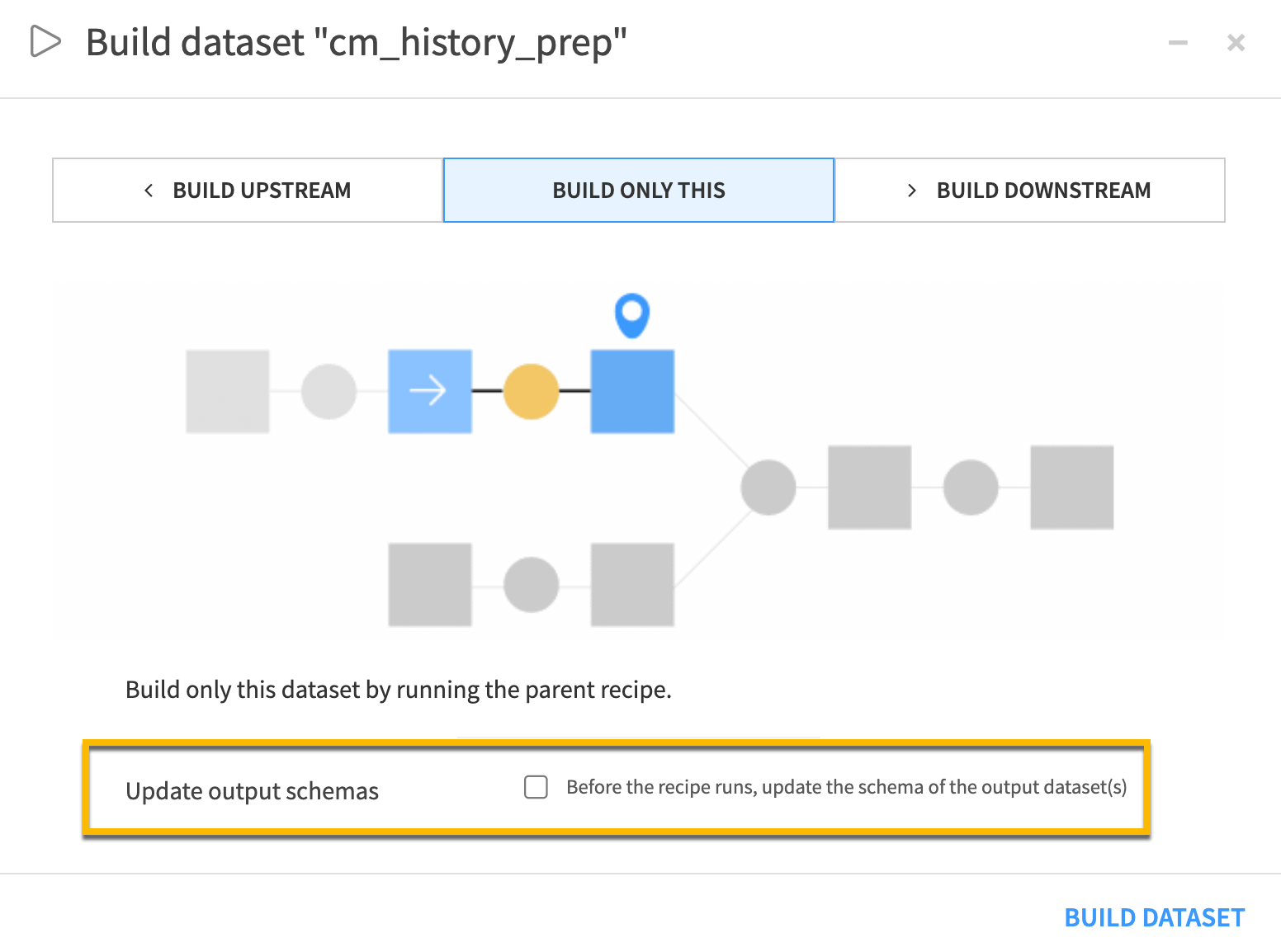
The Update output schemas option propagates the schema to output datasets before each recipe runs. This way, your data will have the latest structure.
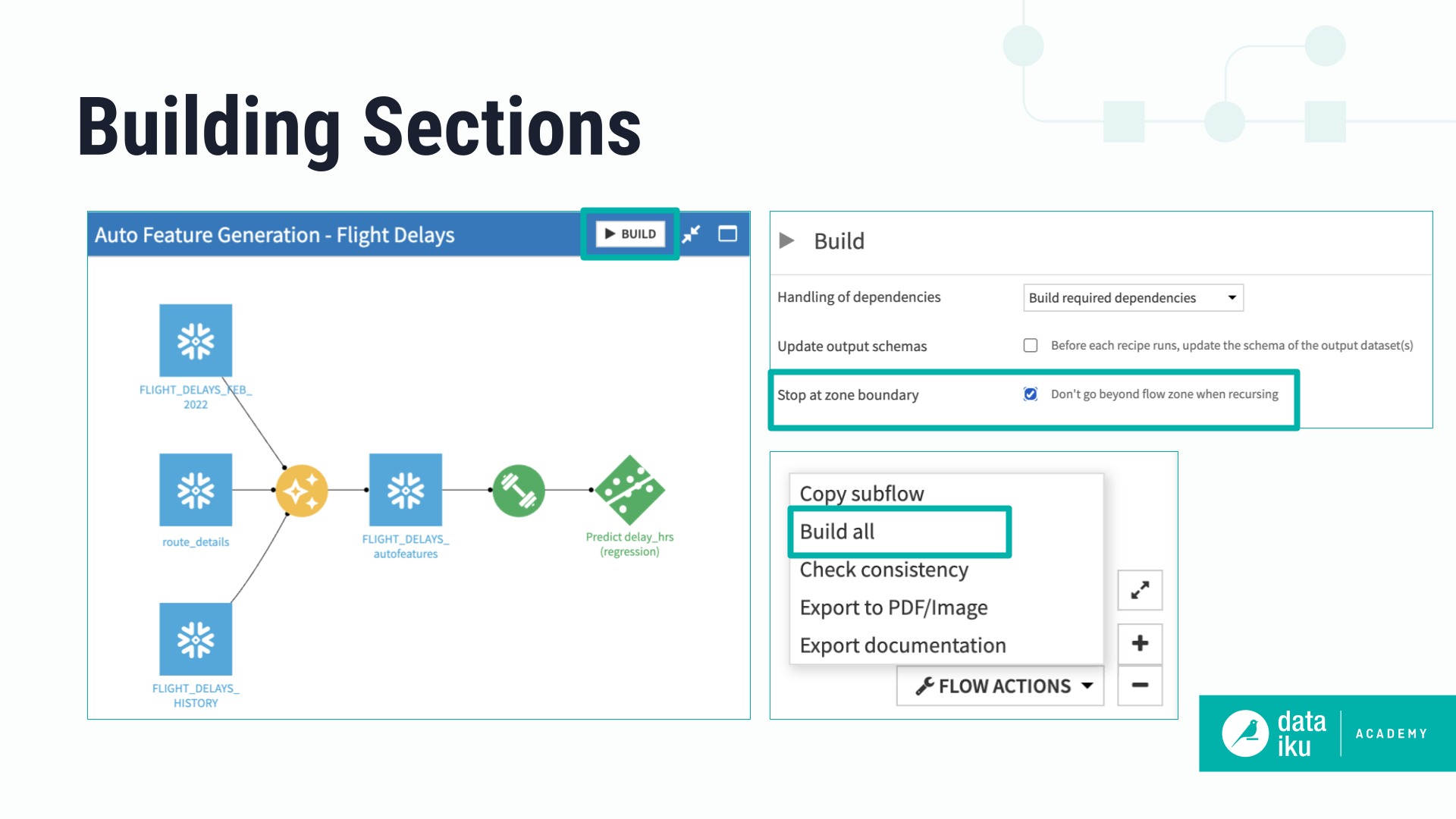
Building sections of the Flow#
You can build the entire Flow using the Build all button in the Flow Actions menu. If you prefer, you can build a specific Flow zone using the Build button directly on the Flow zone instead.
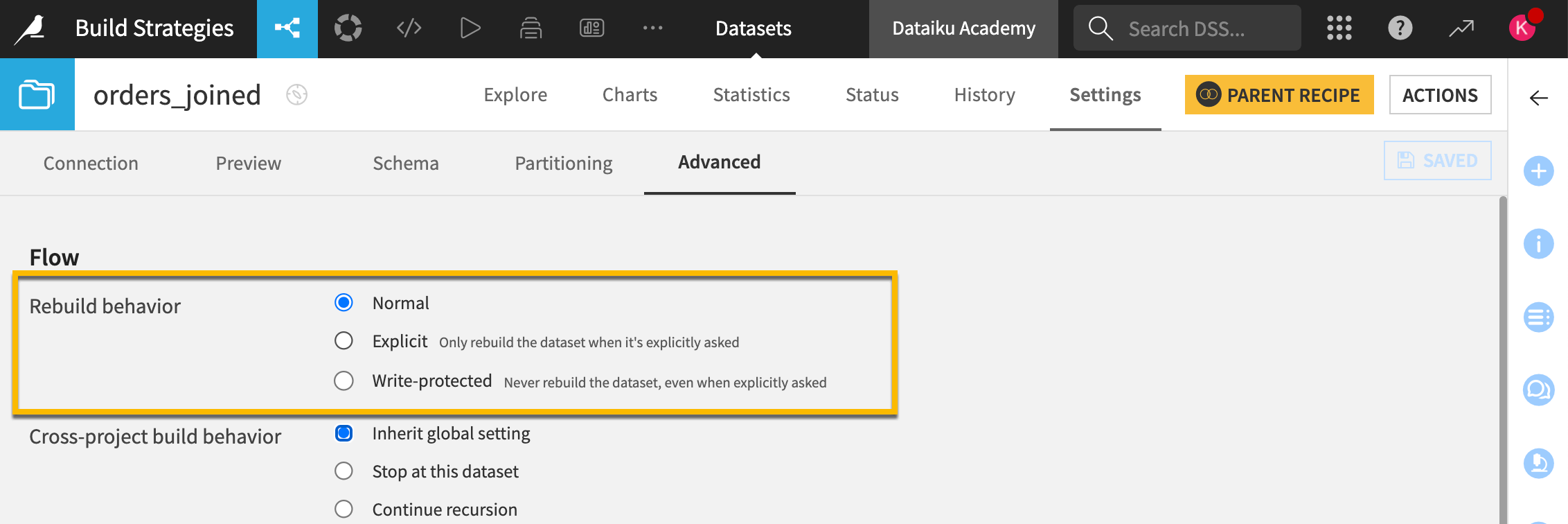
Advanced rebuild behavior#
The Rebuild behavior of a dataset grants control how or if it’s possible to build that dataset.
For one, if you set the rebuild behavior of a dataset to Explicit, the dataset won’t be rebuilt unless you specifically choose to rebuild it. You can also make a dataset Write-protected so it never gets rebuilt.
Next steps#
Now that you’ve explored different build modes and configurations, you may want to try this out for yourself in Tutorial | Build modes!
See also
If you’re curious about automating builds, that will be covered in the Data Quality & Automation course.