Concept | Automation scenarios#
Watch the video

Scenarios are key to automating tasks related to Dataiku projects. Let’s learn about the different types of scenarios and their various components.
Use cases#
Automation scenarios are a set of actions that you can schedule to run when certain conditions are satisfied. They’re most useful when automating various kinds of tasks when a project is in production. For example:
If new data arrives on a regular basis, a scenario can rebuild the Flow once per day or each time it detects a dataset change.
If a metric for a machine learning model falls outside a specified threshold range, a scenario can trigger a job to retrain the model.
Scenarios can also automate administrative tasks such as cleaning logs or starting and stopping a cluster.
Scenario types#
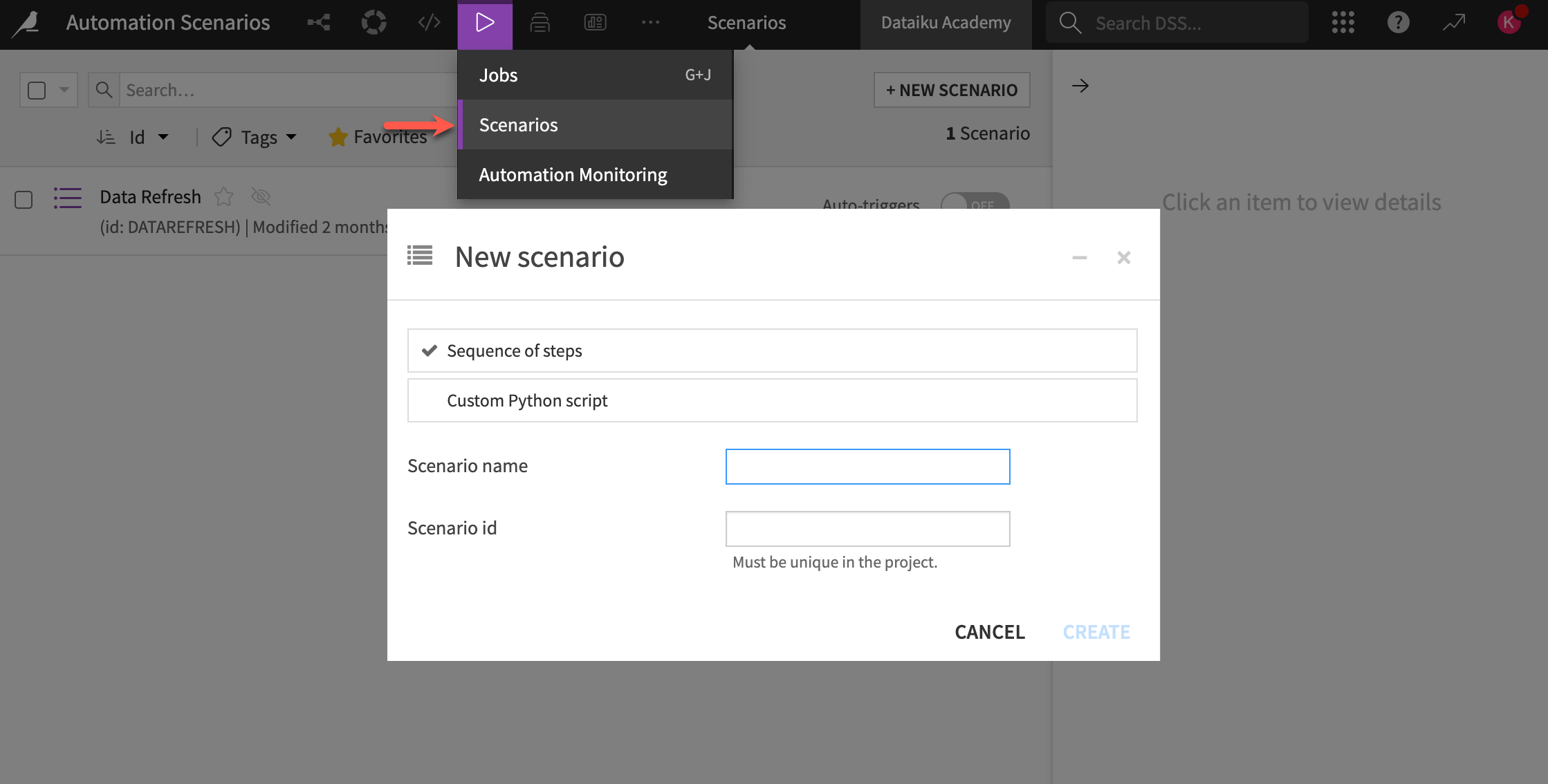
There are two types of scenarios in Dataiku:
Scenario type |
Contents |
|---|---|
Step-based |
You configure scenario steps using a visual interface. |
Code-based |
You fully define the set of actions to occur using Python. |
See also
Learn more about custom Python script scenarios in Concept | Custom metrics, checks, data quality rules & scenarios.
Scenario components#
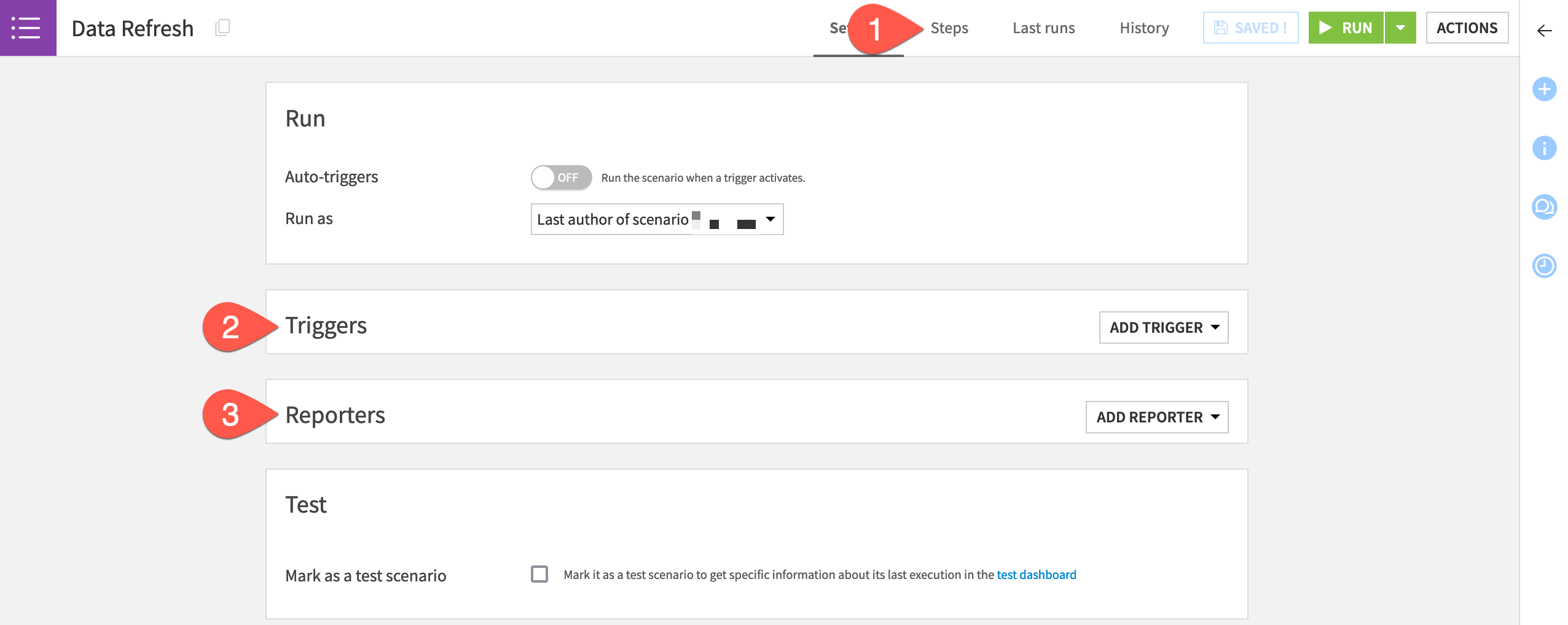
Scenarios consist of three main components:
Component |
Function |
|---|---|
Steps |
Define the series of actions to take when the scenario executes. |
Triggers |
Control when a scenario executes. |
Reporters |
Send alerts about a scenario’s activity via a variety of information channels. |
Scenario steps#
Scenario steps let you control what the scenario will do. Common scenario steps include:
Building or clearing a dataset.
Training a model.
Verifying data quality rules or running checks.
Sending messages.
Refreshing the cache of charts and dashboards.
Exporting documentation of the Flow or models.
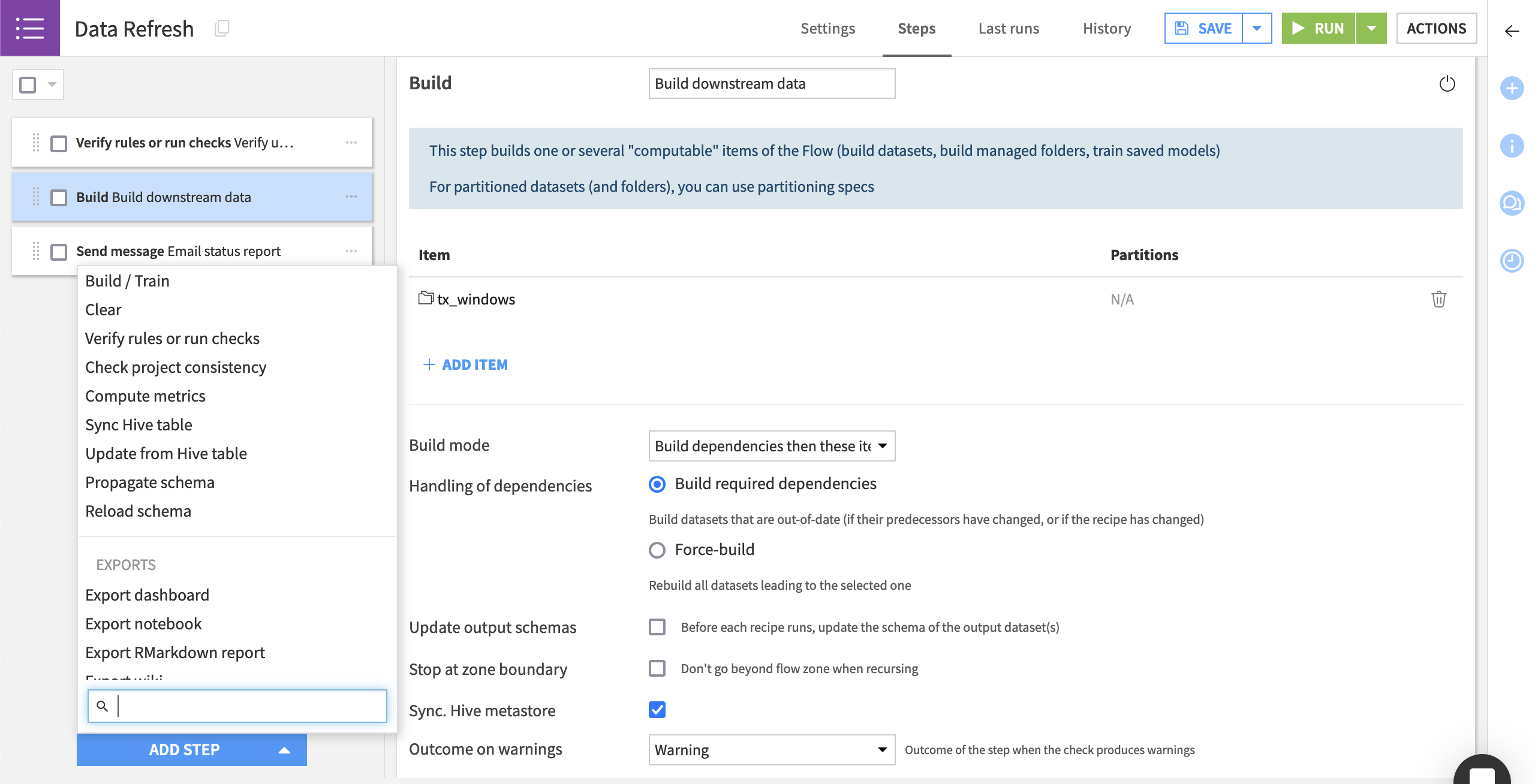
Scenario steps run sequentially. However, you can control whether a step runs based on the outcome of a data quality rule or a check.
See also
See Scenario steps in the reference documentation for the complete list of steps.
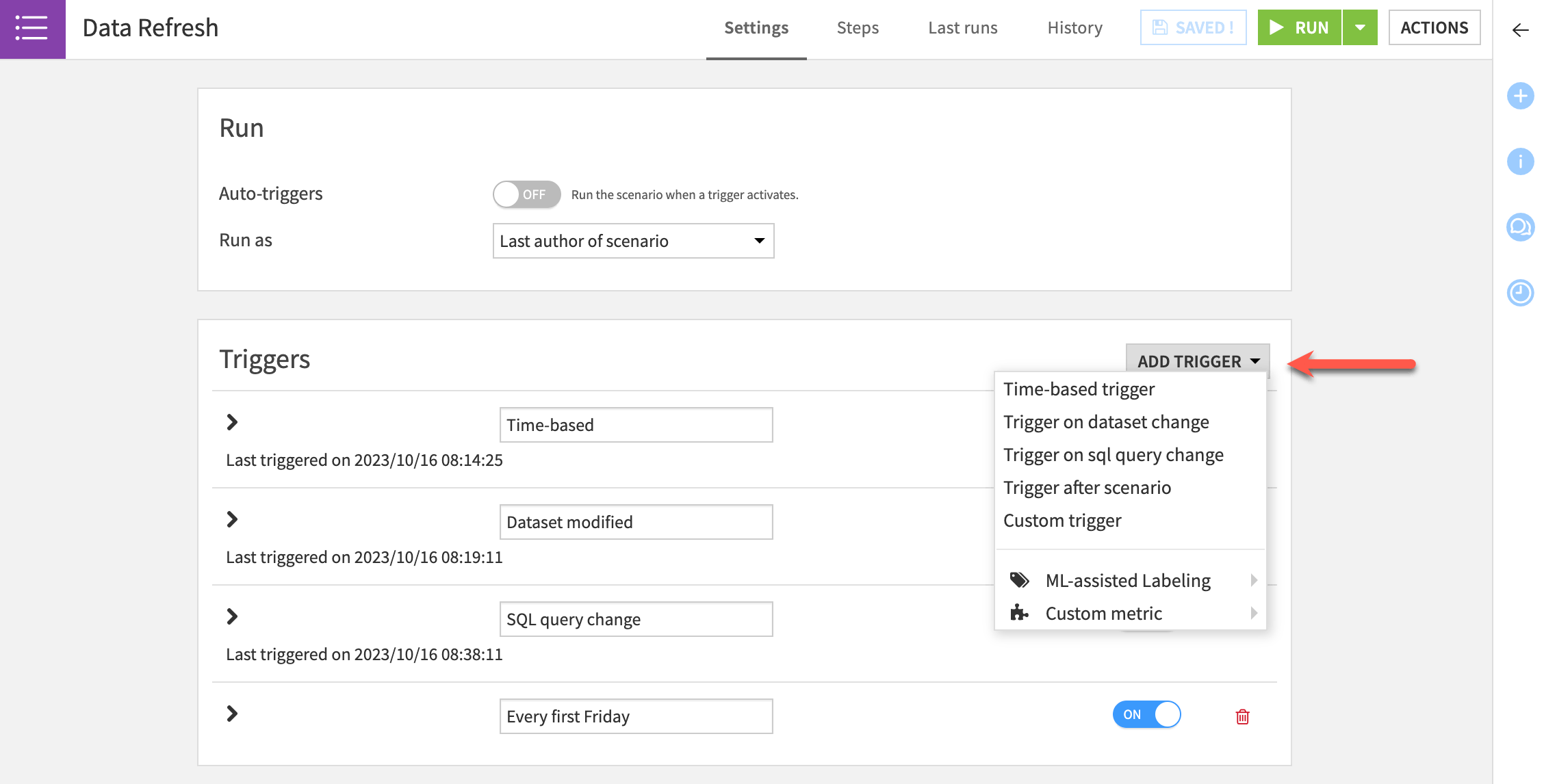
Scenario triggers#
Triggers allow users to define a condition or set of conditions that, if satisfied, start a scenario run. You can turn each trigger on or off.
Trigger |
Description |
|---|---|
Time-based |
Launches the scenario at regular intervals (such as daily). |
Dataset change |
Starts a scenario whenever it detects a change in the dataset. This type of trigger is used for filesystem-based datasets. |
SQL query change |
Runs a query at a specified interval and starts the scenario when the output of the query changes with respect to the last execution of the query. |
Custom (Python) |
Executes a custom Python script that activates a trigger. |
Note
Different types of triggers may be available depending on your license and profile.
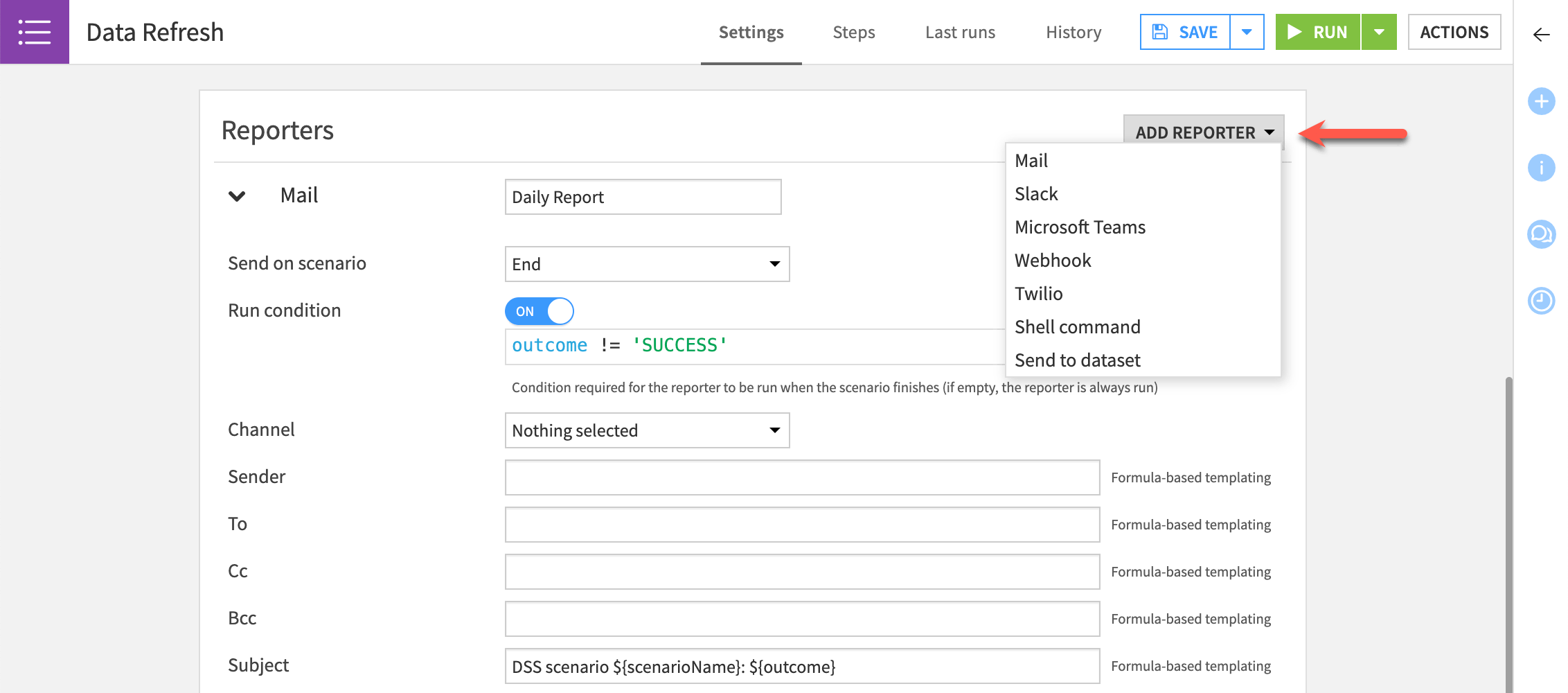
Reporters#
Dataiku lets you add reporters to a scenario to tell users about scenario activities through email and other channels. You can send a reporters when a scenario starts or ends on the condition that it succeeds or fails.
Reporters operate through several channels, including:
Mail
Slack
Microsoft Teams
Webhook
Twilio
Shell command
Send to dataset
Next steps#
Now that you have a better understanding of step-based scenarios in Dataiku, try this out for yourself in Tutorial | Automation scenarios!
See also
Find more information about Automation scenarios in the reference documentation.